Essential Trends in Knowledge Base Construction Research
Organizations see rapid change in knowledge base construction, driven by emerging trends such as AI integration, enhanced user experience, collaboration, security, real-time access, and multimedia. Leading customer service teams rely on knowledge management systems to deliver instant support and boost customer satisfaction. Sobot AI and Sobot call center solutions help unify knowledge, streamline customer service, and improve operational efficiency. Companies in retail, e-commerce, and enterprise services must adopt these knowledge base trends to stay competitive, reduce costs, and increase satisfaction.
AI in Knowledge Base Construction

Automation and NLP
AI technology has transformed knowledge base construction by introducing automation and natural language processing (NLP) into the core of knowledge management. Organizations now use knowledge base tools that leverage machine learning and NLP to understand user queries, automate content creation, and streamline maintenance. These advancements allow knowledge base software to interpret questions in natural language, improving the accuracy and relevance of responses.
Machine learning models continuously learn from user interactions, identifying gaps in knowledge and optimizing content. Automated article generators reduce manual writing, while real-time feedback mechanisms help keep knowledge up to date. AI-powered knowledge base tools also enable faster information retrieval, empowering users to find answers independently and reducing the workload on customer service teams. This shift increases operational efficiency and ensures that knowledge-based software can scale with growing content and user demands.
AI-driven knowledge base construction provides consistent experiences across all customer touchpoints. Enhanced self-service capabilities allow users to resolve issues without waiting for support, which improves satisfaction and reduces costs. Scientific research confirms that AI technologies like NLP and machine learning improve efficiency and accuracy in knowledge management, leading to fewer errors and faster processes.
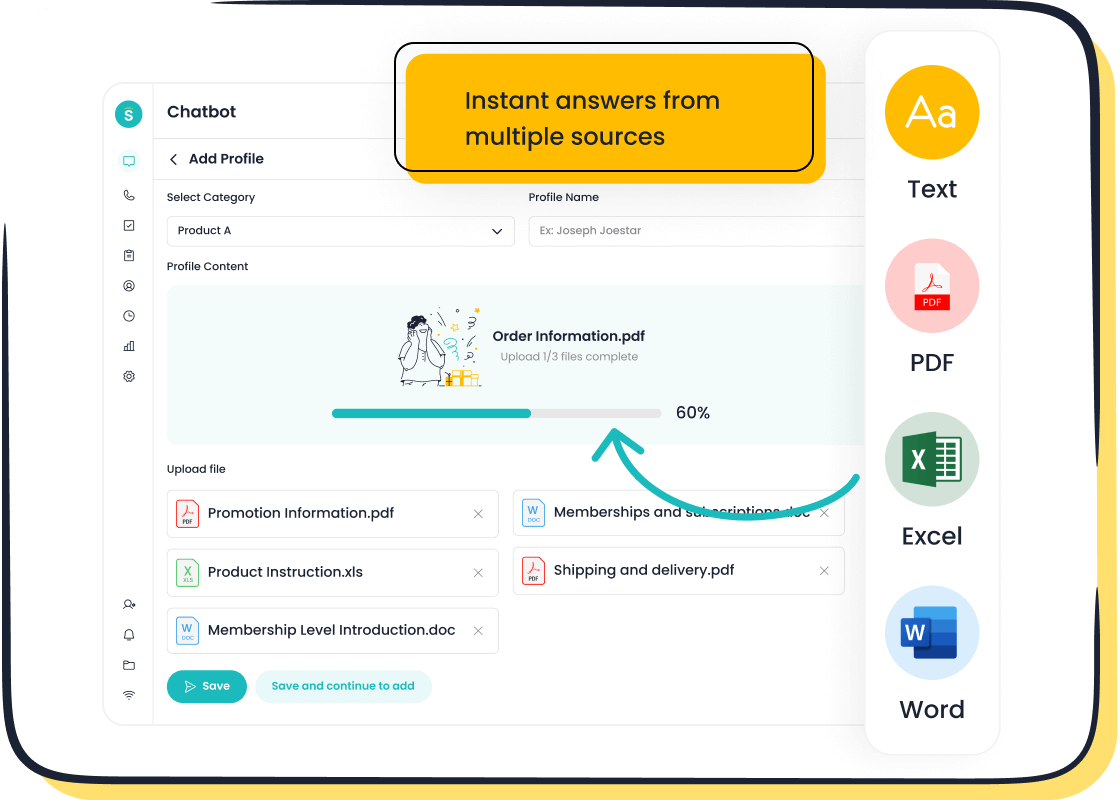
Sobot Chatbot Integration
Sobot’s AI Chatbot exemplifies the power of integrating automation and NLP into knowledge base software. The chatbot operates 24/7, handling regular queries and assisting agents, which boosts productivity by up to 70%. Sobot’s knowledge base tools support omnichannel communication, allowing customers to interact through chat, voice, and social media. The chatbot uses machine learning to learn from uploaded documents and user interactions, ensuring that knowledge remains current and relevant.
A notable example comes from OPPO, a global smart device leader. OPPO implemented Sobot’s chatbot and ticketing system to manage high volumes of customer service inquiries. The result was an 83% chatbot resolution rate and a 94% positive feedback score, demonstrating the effectiveness of AI-driven knowledge base construction. Sobot’s knowledge-based software enabled OPPO to reduce manual maintenance by 90% and increase repurchase rates by 57%. These outcomes highlight how advanced knowledge base software can optimize customer service and drive business results.
User Experience Trends
Personalization
Personalization stands out as one of the most important trends in user experience for knowledge base design. Companies use customer personas to tailor the tone, structure, and content of their knowledge resources. This approach helps users feel understood and valued, which increases customer retention and satisfaction. Modern knowledge base platforms analyze user preferences and behaviors to deliver relevant articles, FAQs, and guides. AI-powered chatbots, like those found in user-friendly knowledge base systems, personalize responses by learning from previous interactions.
- Simplicity and clarity in navigation encourage users to return and engage more deeply.
- Personalized recommendations and content boost engagement by up to 80%.
- Interactive features, such as proactive messaging and real-time assistance, help users solve problems quickly.
- Metrics like session length and conversion rates show how personalization improves customer retention and satisfaction.
Personalization in knowledge base design not only increases engagement but also reduces support costs by anticipating user needs. Companies that focus on emerging trends in personalization gain a competitive advantage and build stronger brand loyalty.
Accessibility
Accessibility ensures that knowledge is available to everyone, including people with disabilities. Modern knowledge base platforms follow standards such as WCAG, ADA, and Section 508 to make content usable for all. Features like alt-text for images, captions for videos, and support for screen readers help users access information easily. Proper heading levels, semantic markup, and clear language make navigation simple for everyone.
- Accessibility features broaden the audience and improve usability for all users.
- Internationalization and localization adapt knowledge content for different languages and cultures, increasing inclusivity.
- Continuous auditing and monitoring help maintain compliance with accessibility standards.
- Inclusive design increases customer retention by making the user experience seamless for diverse groups.
Accessible and user-friendly knowledge base platforms demonstrate organizational commitment to inclusivity and customer satisfaction. By embedding accessibility into workflows, companies ensure that knowledge reaches every user, improving overall satisfaction and retention.
Collaboration in Knowledge Base Trends
Collaboration has become a defining feature of modern knowledge management. Organizations now recognize that a collaborative knowledge base supports accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability. Two main approaches—team authoring and community input—drive these improvements.
Team Authoring
Team authoring brings together experts from different departments to create and maintain knowledge content. This approach ensures that the knowledge base reflects a wide range of expertise and stays relevant as products and services evolve. Teams use advanced tools to streamline collaboration and boost productivity.
| Collaboration Benefit | Description | Example Tool(s) & Features |
|---|---|---|
| Better Team Communication | Real-time commenting and discussions reduce email overload. | ClickHelp (real-time commenting), Confluence (discussion threads) |
| Increased Productivity | Simultaneous editing, task assignment, and notifications speed up workflows. | Google Docs, ClickHelp, Confluence |
| Centralized Knowledge Management | A central repository improves access and onboarding. | ClickHelp, Confluence, Document360 |
| Flexibility and Accessibility | Cloud-based tools enable collaboration from any device. | Google Workspace, Notion |
| Security and Compliance | Data encryption and role-based access protect sensitive information. | ClickHelp, Confluence |
Collaborative features such as real-time editing, autosave, versioning, and AI-powered writing assistants help teams keep knowledge accurate and up to date. Organizations that use these tools report faster content updates and improved searchability, which leads to higher productivity and reduced costs.
Community Input
Community input plays a vital role in maintaining a relevant and effective knowledge base. Users contribute by asking questions, sharing tips, and suggesting fixes. This feedback loop helps organizations identify gaps and address real user needs.
- Community sections allow users to share experiences and solutions, reducing the workload for support teams.
- Article scoring and suggestions keep knowledge aligned with current trends and user expectations.
- Regular updates based on user feedback ensure the knowledge base evolves with products and services.
- Focusing on user pain points leads to clear, practical, and user-friendly content.
Organizations that encourage community participation see measurable benefits. For example, introducing a collaborative knowledge base can reduce customer churn by 20% and cut search times by 60%. Regular audits and metadata systems further improve accuracy and efficiency, supporting a living knowledge base that adapts to change.
Security and Privacy
Data Protection
Organizations must protect sensitive information stored in their knowledge base software. Security threats continue to evolve, targeting both data and infrastructure. Common risks include phishing, ransomware, insider threats, and malware. Recent incidents, such as supply chain attacks and vulnerabilities in popular software, highlight the need for robust security measures.
| Security Threats | Description | Effective Mitigation Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing Attacks | Trick users into revealing sensitive information. | Email filtering, security awareness training, MFA. |
| Ransomware | Encrypt data and demand ransom for decryption. | Data backups, threat detection, employee vigilance. |
| Insider Threats | Malicious or accidental actions from within the organization. | Role-based access control, audit trails, strict access policies. |
| Malware | Infiltrate systems with harmful software. | Antivirus, firewalls, regular software updates. |
| Data Breaches | Unauthorized access to sensitive data. | Data encryption, access controls, risk assessments. |
To safeguard knowledge, organizations should:
- Select SOC 2 compliant providers for strong security controls.
- Use strict access permissions and zero trust models.
- Educate employees on cybersecurity best practices.
- Monitor systems continuously for suspicious activity.
- Vet software integrations to prevent vulnerabilities.
- Request regular security reports from providers.
Security awareness training and simulated phishing drills help employees recognize threats and reduce risk. Strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regular software updates further protect knowledge base software from attacks.
Compliance
Compliance regulations shape how organizations build and maintain their knowledge bases. Laws and standards require companies to document safety, environmental, and ethical practices. Regulatory bodies such as OSHA and EPA set rules for workplace safety and environmental protection. Knowledge base software must support version control, audit trails, and regulatory updates.
- Building and environmental regulations require training on waste management and hazardous substances.
- Health and safety laws mandate risk assessments and worker safety plans.
- Employment laws ensure fair wages and safe working conditions.
- Financial crime regulations demand anti-money laundering and transaction monitoring.
- Legal compliance covers contract law, property law, and tax requirements.
Organizations face challenges such as changing regulations, complex standards, and resource constraints. They address these by monitoring updates, providing training, using compliance tracking software, and maintaining centralized documentation. Regular risk assessments and audits ensure that knowledge remains accurate and actionable.
Compliance specialists and legal counsel help organizations stay informed and reduce legal risks. Continuous learning and collaboration embed compliance knowledge into daily operations, supporting resilience and ethical business practices.
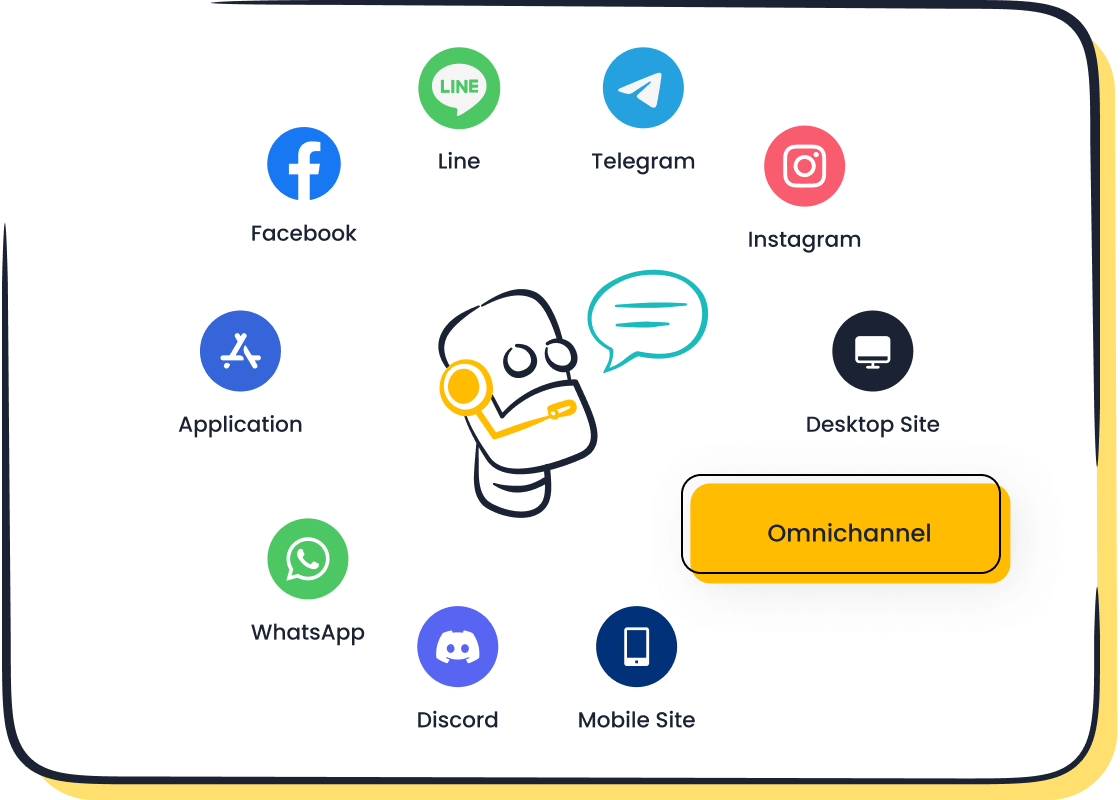
Real-Time and Omnichannel Access
Self-Service
Self-service has become a cornerstone of modern customer support. Customers expect to solve problems independently, using self-service options that provide instant access to knowledge. Many users prefer digital self-service support over traditional channels. Businesses see benefits such as reduced ticket volume, lower operational costs, and improved customer satisfaction. Self-service knowledge base tools empower customers to find answers without waiting for an agent. This shift allows support teams to focus on complex issues.
- Customers access real-time information through knowledge base portals, reducing wait times and repetitive queries.
- Self-service options enable users to resolve issues anytime, increasing convenience and retention.
- AI-powered chatbots deliver accurate knowledge instantly, improving resolution speed and customer experience.
- Centralized and updated knowledge bases help agents and customers find solutions faster.
A well-structured self-service portal must offer clear, jargon-free content. Continuous updates and quality control ensure the knowledge remains relevant. Businesses that invest in self-service support see higher satisfaction rates and lower costs. For example, 31% of users prefer digital self-service, while 27% favor a hybrid approach. These trends highlight the importance of self-service in customer support environments.
Sobot Omnichannel Solutions
Sobot’s omnichannel solutions unify customer interactions across email, chat, social media, voice, and web platforms. The platform integrates all customer channels into a single AI-powered contact center, providing seamless access to knowledge base tools. Customers can switch between channels without losing context, ensuring consistent self-service experiences.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Unified Agent Workspace | Agents manage all interactions in one interface |
| Intelligent Search | Customers find relevant knowledge quickly |
| Real-Time Analytics | Businesses optimize support performance |
| Multi-Language Support | Personalized self-service options for global users |
| Scenario-Based AI | Accurate and efficient delivery of knowledge |
Sobot’s knowledge base portal includes self-service options such as FAQs and AI chatbots. These tools empower customers to resolve issues independently, reducing support workload. Real-time information and omnichannel routing improve response times and resolution rates. Sobot’s platform supports seamless customer experiences, increasing satisfaction and loyalty. Businesses in retail and e-commerce benefit from Sobot’s ability to deliver knowledge across multiple touchpoints, optimizing both support and operational efficiency. Learn more about Sobot’s omnichannel solutions.
Multimedia Content
Video and Audio
Video and audio formats have become essential in modern knowledge bases. These formats help users understand complex topics by engaging both visual and auditory senses. When organizations add videos, podcasts, or audio guides to their knowledge resources, they make learning more memorable and enjoyable. Research shows that combining video and audio increases knowledge retention and user engagement. This approach supports different learning styles, so visual learners benefit from videos, while auditory learners gain from audio narration or podcasts.
- Multimedia content breaks up long text, making knowledge easier to absorb.
- Captions, transcripts, and alternative formats support accessibility for all users.
- Videos can show step-by-step processes, helping users solve problems quickly.
- Audio guides allow users to learn on the go, using mobile devices.
Multimedia design should balance visual and auditory elements to avoid overwhelming users. When done well, it motivates learners and improves their problem-solving skills. Studies confirm that students who use video and audio in knowledge bases perform better and feel more satisfied.
Interactive Knowledge
Interactive features transform a knowledge base from a static resource into an engaging learning environment. Tutorials, infographics, and interactive guides encourage users to participate actively. Gamification elements, such as badges and leaderboards, motivate users to explore more knowledge and return often. Community-driven content, like forums and Q&A sections, lets users share their experiences and solutions, building trust and improving the quality of knowledge.
| Interactive Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Tutorials & Walkthroughs | Guide users through complex tasks |
| Gamification | Increases motivation and session duration |
| Community Q&A | Enhances content with real user insights |
| Feedback Tools | Improves knowledge through user suggestions |
Organizations track the effectiveness of multimedia and interactive knowledge by monitoring article views, search success rates, and user feedback. These key performance indicators help teams update content and ensure users find the knowledge they need quickly. Mobile-friendly and accessible design further expands the reach of knowledge bases, supporting users everywhere.
Future of Knowledge Management
LLMs and RAG
Large language models (LLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) are shaping the future of knowledge management. LLMs can process and generate human-like text, but RAG takes this further by connecting these models to external knowledge bases. This combination improves the accuracy and credibility of responses, especially for knowledge-intensive tasks. RAG enables continuous updates and domain-specific integration, merging the internal knowledge of LLMs with dynamic external databases. Organizations use RAG to build knowledge bases that support real-time information retrieval and provide up-to-date answers.
Recent research shows that RAG methods help organizations construct and complete knowledge bases more efficiently. For example, companies store semantic embeddings of text in vector databases, which allows LLMs to retrieve relevant knowledge based on meaning rather than keywords. This approach overcomes token limits and ensures that users receive accurate, context-aware responses. In practice, RAG has improved question-answering accuracy and relevance, making it a valuable tool for modern knowledge management systems.
Organizations that invest in LLMs and RAG prepare for the future of knowledge management by enabling smarter, more adaptive knowledge solutions.
Semantic Data
Semantic data plays a vital role in enhancing the searchability and relevance of knowledge base content. Instead of relying on exact keyword matches, semantic search interprets the meaning behind queries. It uses vector search to transform both queries and documents into embeddings, ranking results based on conceptual relevance. This method considers user intent, location, and search history, delivering more accurate and personalized results.
- Semantic data helps systems understand user intent and context.
- Knowledge graphs organize information by meaning, revealing connections between data points.
- Inference engines apply logical rules to expand query understanding.
- Vector embeddings enable similarity searches, finding relevant knowledge even without exact matches.
By adopting semantic data structures, organizations improve multi-hop reasoning, entity disambiguation, and efficient retrieval. These advances support the future of knowledge management by making knowledge bases more intelligent and user-focused.
The table below summarizes predicted trends and organizational strategies for the future of knowledge management:
| Predicted Future Trend | Description | How Organizations Are Preparing |
|---|---|---|
| Integration of AI and Machine Learning | KM systems analyze big data in real-time and filter relevant knowledge using AI tools. | Organizations deploy AI widely, align initiatives with business goals, and engage employees. |
| Use of Knowledge Graphs | Model complex relationships to improve context-aware knowledge delivery. | Businesses adopt knowledge graphs for dynamic KM systems. |
| Embedding KM into Business Processes | Integrate KM into workflows for efficiency and innovation. | Teams use KM tools that surface relevant knowledge during key processes. |
| Digital Collaboration for Remote/Hybrid Work | Use digital tools to capture and share tacit knowledge. | Organizations implement asynchronous platforms and AI transcription tools. |
| Addressing Challenges | Use curation and change management to overcome barriers. | AI-driven tagging, recommendations, and change management plans are employed. |
Organizations see clear benefits when they embrace trends in knowledge base construction. AI, user-centered design, and omnichannel strategies improve customer service, satisfaction, and customer retention. Companies report higher customer satisfaction and faster support when they use advanced knowledge management tools. Security and continuous training protect knowledge and support business growth. Leaders should evaluate current knowledge management systems, organize knowledge logically, and train teams to use new technology. These steps help businesses deliver better customer service and maintain satisfaction.
FAQ
What is a knowledge base and why do organizations need it?
A knowledge base is a digital library of information. Organizations use knowledge base software to store, organize, and share answers. This helps teams solve problems faster and improves customer service.
How does AI improve knowledge base construction?
AI automates content creation and updates. Knowledge base tools with AI use machine learning and natural language processing. These features help knowledge management teams keep information accurate and easy to find.
What features should effective knowledge base software include?
Effective knowledge base software should offer search, real-time updates, user-friendly design, and security. It should support multimedia, team collaboration, and compliance. These features make knowledge base construction efficient and reliable.
How do knowledge base tools support omnichannel customer service?
Knowledge base tools connect with chat, email, voice, and social media. This integration gives customers instant access to information across channels. Omnichannel support improves knowledge management and customer satisfaction.
Why is security important in knowledge base management?
Security protects sensitive data in the knowledge base. Organizations use encryption, access controls, and compliance checks. These steps keep knowledge base software safe and trustworthy for users.
See Also
Comprehensive Overview Of Quality Management Systems In Call Centers
Best Artificial Intelligence Solutions For Enterprise Contact Centers
Leading Speech Analytics Software Options For Call Centers 2024
How To Select The Most Effective Chatbot Software Solutions
Essential Best Practices For Managing Quality In Call Centers
