How Different Methods Uncover Customer Pain Points

Understanding customer pain points shapes business outcomes in retail, e-commerce, and customer support. When a customer faces slow support, confusing processes, or limited feedback options, satisfaction and loyalty drop. For example, long wait times or complex ordering systems often lead to lost sales. Sobot and Sobot AI offer solutions that help identify these issues through customer pain point research. Many brands now rely on the Sobot call center to resolve customer problems quickly and improve the overall experience.
Customer Pain Point Impact on Business Outcomes Ineffective Communication Loss of trust, lower satisfaction, reduced loyalty Process Pain Points Cart abandonment, customer churn, lost revenue Support Pain Points Reduced trust, increased customer churn
Why Customer Pain Point Research Matters
Impact on Customer Experience
Customer pain point research helps brands understand what customers struggle with during their journey. When companies listen to feedback and identify pain points, they can improve the customer experience. For example, if a retail store finds that long checkout times frustrate shoppers, it can add more staff or self-checkout options. This change increases customer satisfaction and makes people more likely to return.
73% of consumers say a good experience locks in brand loyalty (Forbes).
Companies like Sobot use tools such as surveys and analytics to track customer satisfaction scores, like NPS and CSAT. By addressing pain points, brands turn unhappy customers into loyal fans. This process also helps companies spot trends and act quickly to improve the overall experience.
Business Value of Addressing Pain Points
Addressing customer pain points leads to better business results. When companies solve problems, they build trust and loyalty. Satisfied customers are more likely to buy again and recommend the brand to others. For example, 32% of customers would leave a brand after one bad experience (PWC).
Sobot’s solutions help businesses automate support and gather feedback, making it easier to fix issues fast. This approach leads to higher customer satisfaction, stronger relationships, and steady growth. Companies that focus on customer pain point research often see increased revenue and long-term success.
Role in Customer Support and Contact Centers
Customer support teams play a key role in finding and solving pain points. When agents use tools like the Sobot Ticketing System, they can track common problems and respond faster. This system lets agents see all customer information in one place, making support more personal and efficient.
Tip: Giving agents access to customer history and feedback helps them solve issues quickly and improve satisfaction.
Support teams that focus on customer pain points can fix root causes, not just symptoms. This leads to better service, happier customers, and fewer repeat problems. Companies that use customer pain point research in their contact centers often see higher satisfaction scores and lower churn rates.
Main Approaches to Customer Pain Points
Businesses use several main approaches to uncover customer pain points. These methods help companies understand what customers experience and why they face certain problems. By combining different techniques, organizations can get a full picture of customer needs and improve their services.
Qualitative Research Methods
Qualitative research methods focus on understanding the reasons behind customer pain points. Companies often use interviews, usability testing, and contextual inquiries. For example, user interviews allow one-on-one conversations where customers share their struggles. Usability testing lets researchers watch customers as they use a product or service, revealing where they get stuck. Contextual inquiries involve observing customers in real-life settings to find hidden issues. Empathy maps and affinity diagrams help teams organize and visualize customer feedback, making it easier to spot patterns. These methods provide deep insights into emotions and behaviors that numbers alone cannot show.
| Strengths of Qualitative Research Methods | Weaknesses of Qualitative Research Methods |
|---|---|
| Uncovers deep, nuanced insights | Can introduce researcher bias |
| Flexible and adaptable | Time-consuming process |
| Highlights participant voices | Needs skilled analysts |
| Allows real-world validation | Balancing insight with reliability |
Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods use numbers and data to identify customer pain points. Surveys are a popular tool because they collect large amounts of information quickly. Companies also use A/B testing to compare different versions of a website or app. Funnel analysis tracks where customers drop off during a process, such as checkout. Heatmaps and session recordings show how customers interact with digital platforms. These methods help businesses see patterns, measure the size of a problem, and make decisions based on facts. For example, a survey might reveal that 30% of customers abandon their carts at checkout, signaling a pain point that needs attention.
Internal Feedback from Support Teams
Support teams interact with customers every day. They hear about recurring problems and can spot trends early. When support agents document common complaints, companies can identify and address customer pain points faster. Training agents to recognize and report these issues improves service quality. Tools like the Sobot Ticketing System help by collecting and analyzing pain points from every channel. This system organizes customer feedback, making it easy to track and resolve issues. Conversation intelligence tools also analyze calls and messages, helping teams find emotional cues and recurring problems. By using internal feedback, companies can fix issues before they grow.
Jobs-to-be-Done in Customer Pain Point Research
Definition and Key Concepts
The jobs-to-be-done (JTBD) framework helps teams understand what customers want to achieve in their daily lives. JTBD looks beyond product features and focuses on the tasks, or "jobs," customers try to complete. These jobs include functional, emotional, and social aspects. For example, a finance manager using software may want to finish reports quickly (functional), feel less stressed (emotional), and look competent to others (social). Customer pain point research uses JTBD to uncover the challenges customers face while trying to get these jobs done. By understanding customer needs in this way, companies can design better solutions. JTBD statements describe the situation, the job, the desired outcome, and the pain points. This approach helps teams see products as tools customers "hire" to solve problems, making it easier to spot unmet customer needs and improve satisfaction.
Steps for Implementation
To use JTBD in customer pain point research, teams follow a series of steps:
- Define the market by focusing on the job customers want to accomplish, not just the product. Use tools like the JTBD Market Definition Canvas to shift from product thinking to problem solving.
- Map the customer’s job using an eight-step job map: Define, Locate, Prepare, Confirm, Execute, Monitor, Modify, and Conclude. This map shows the order of tasks and highlights pain points.
- Conduct interviews with real customers. Ask them to share stories about their experiences, struggles, and needs at each step.
- Identify different personas, such as the job executor, support team, and buyer. Each persona has unique needs and perspectives.
- Prioritize which jobs and pain points to address based on customer insights and business goals. Use methods like cost of delay analysis to help decide.
- Develop and test solutions. Form hypotheses about how to solve pain points, then run experiments to see what works best.
This process ensures that customer pain point research uncovers real needs and guides product development.
Strengths and Limitations
The JTBD framework offers several strengths and some limitations when used in customer pain point research:
| Strengths of JTBD Framework | Limitations of JTBD Framework |
|---|---|
| Focuses on customer-centric goals and solution-neutral jobs, enabling innovation. | Risk of over-abstraction, which can lead to vague insights. |
| Provides strategic clarity and helps teams align around customer needs. | May neglect emotional and UX aspects if focusing only on functional jobs. |
| Supports continuous product improvement by identifying unmet needs and adjacent jobs. | Requires deep qualitative research, which can be resource-intensive. |
| Helps teams communicate customer needs clearly across departments. | Customers may have limited experience, restricting the scope of innovation. |
| Enables companies to uncover real pain points and prioritize innovation. | Can be difficult to capture subconscious expectations and deeper emotional needs. |
JTBD helps teams focus on what matters most to customers. However, teams must balance functional, emotional, and social needs to avoid missing important insights. Sobot uses JTBD principles to help businesses in retail and e-commerce identify and address customer pain points, ensuring solutions meet real customer needs and improve satisfaction.
Pain Point Mapping for Customer Support

What Is Pain Point Mapping
Pain point mapping gives customer support teams a clear way to see where customers struggle. Teams collect and organize feedback, surveys, and interactions into categories. These maps show common customer pain points, such as long wait times or confusing instructions. By visualizing these challenges, teams can spot patterns and focus on the most urgent issues. Pain point mapping also helps different departments, like marketing and sales, work together to create better solutions. When teams update maps regularly, they keep up with changing customer needs and improve satisfaction. This process encourages empathy, as teams view service pain points from the customer’s perspective and turn abstract frustrations into clear actions.
How to Create a Pain Point Map
Teams follow several steps to build effective pain point maps:
- Gather customer experience data using surveys, interviews, and sentiment analysis.
- Map out each stage of the customer journey, such as Awareness, Decision, and Retention.
- Identify and prioritize customer pain points by looking for moments of frustration or roadblocks.
- Use empathy by experiencing the journey themselves to understand real frustrations.
- Make the pain point map a shared document so all departments can contribute.
- Segment maps to focus on specific goals, like reducing wait times or improving payment options.
- Prioritize the most influential pain points to use resources wisely.
Teams can also create lists of customer questions, group them by type, and brainstorm solutions. Documenting the process with notes and photos helps keep insights fresh.
Benefits and Drawbacks
Pain point mapping offers many benefits. It helps teams find and remove roadblocks, highlights weaknesses, and shows how to fix them. By seeing from the customer’s view, teams can improve retention and satisfaction. Maps also help companies make better decisions and set stronger goals. However, pain point mapping has some drawbacks. It needs support from many departments, which can be hard if teams work in silos. If not updated, maps may become outdated or ignored. Some customers do not follow the mapped journey, so maps might miss certain frustrations. Too much data can also make decision-making harder.
Note: Pain point mapping supports a customer-centric approach and helps prevent churn by focusing on critical issues that reduce loyalty.
Using Sobot Ticketing System for Pain Point Mapping
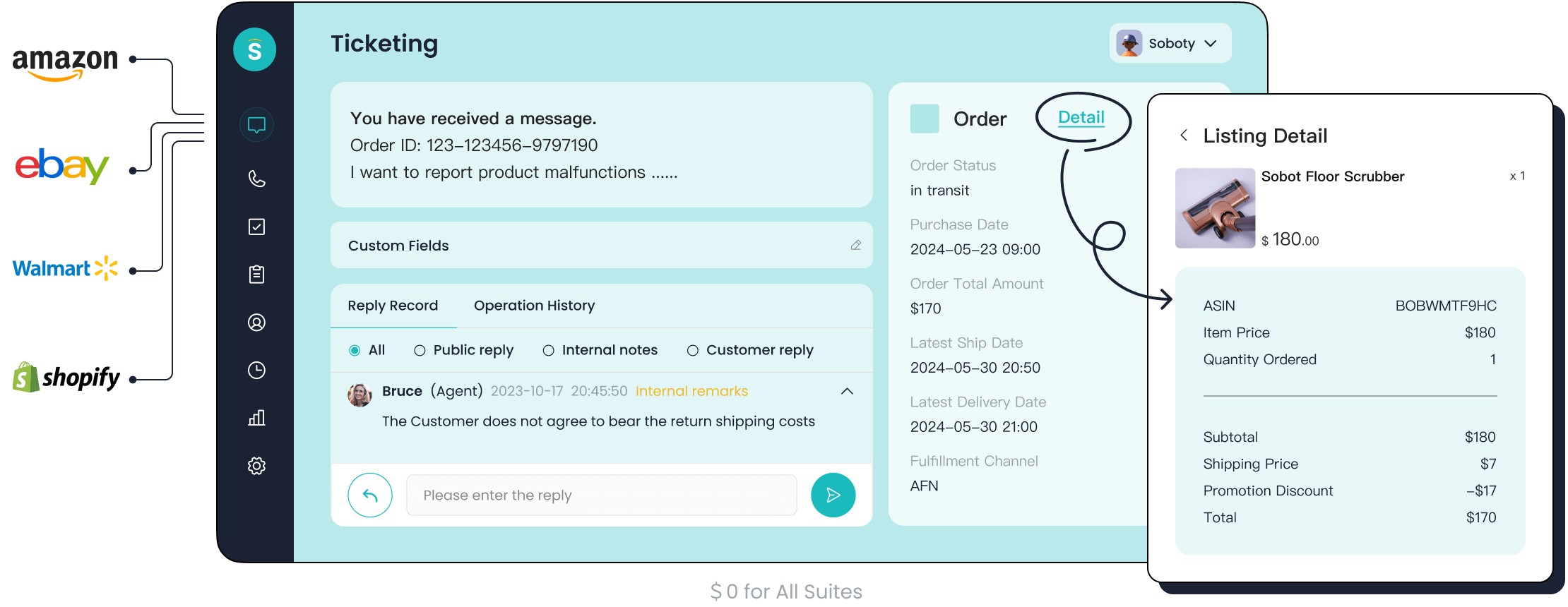
The Sobot Ticketing System makes pain point mapping easier for support teams. It collects feedback from email, chat, and voicemail in one place. The system uses AI to group similar tickets and highlight common customer pain points. Teams can view maps of issues by category, urgency, or channel. Sobot’s analytics help teams track trends and measure the impact of solutions. With multilingual support, Sobot ensures feedback from global customers is included in the maps. By using Sobot, companies can update pain point maps quickly and share them across departments, leading to faster improvements and higher customer satisfaction.
Customer Journey Maps and Pain Points

Overview of Customer Journey Maps
Customer journey maps show every step a customer takes when interacting with a brand. These maps help businesses see the full path, from first learning about a product to after making a purchase. Each map highlights the different touchpoints where customers connect with the company. By mapping the journey, teams can understand customer emotions, motivations, and frustrations at each stage. The maps create a visual story that makes it easier to spot customer pain points and see where improvements are needed. Companies like Sobot use journey maps to better understand customer needs and deliver a smoother experience across all channels.
Identifying Pain Points Along the Journey
Identifying touchpoints is the first step in finding customer pain points. Teams study each stage of the journey by collecting feedback through surveys, interviews, and support logs. They watch for moments when customers feel confused, frustrated, or stuck. For example, slow website loading or unclear instructions often cause problems. By analyzing support tickets and complaints, businesses can see which touchpoints need attention. Journey maps help teams organize this information and update it as customer needs change. Regular testing and feedback keep the maps accurate and useful. Sobot’s Ticketing System helps companies track and group pain points, making it easier to spot trends and act quickly.
Applications in E-commerce and Retail
E-commerce and retail companies use customer journey maps to improve the customer experience and boost results. These maps reveal where customers drop off, such as during checkout or when searching for products. Behavior analytics, like clicks and scrolls, show hidden pain points at different touchpoints. Support logs and chat transcripts highlight common questions and frustrations. Surveys and funnel analysis help teams see where customers leave the journey. For example, Nordstrom used journey maps to create a “reserve online, try in-store” option, raising conversion rates to 60%. Sephora improved its loyalty program by mapping the journey, increasing engagement by 45% (Loyalty360). Companies that use journey maps often see higher retention and lower service costs. Sobot’s solutions help retail and e-commerce brands gather data from all touchpoints, making it easier to update maps and meet customer needs.
Comparing Customer Pain Point Research Methods
Similarities and Differences
Customer pain point research uses many methods to find out what customers need and where they struggle. Each method helps teams see the journey from a different angle. Some methods collect direct feedback, while others observe behavior or test new ideas. The table below shows how these methods compare:
| Research Method | Similarities | Differences |
|---|---|---|
| Surveys and Feedback Forms | Collect direct customer feedback; can include structured and open-ended questions | Suitable for larger samples; structured or semi-structured data collection |
| User Interviews and Focus Groups | Provide qualitative, in-depth insights; allow exploration of context and emotions | Smaller participant groups; deeper, contextual understanding |
| Social Media Listening and Analytics | Indirect, observational data collection; identify recurring complaints publicly | Data is passive and unstructured; relies on monitoring online behavior and conversations |
| Prototype Testing and A/B Testing | Experimental methods focused on product development; test solutions to pain points | More controlled, experimental settings; focus on product iterations and performance comparison |
All these methods aim to uncover pain points by gathering feedback or watching how people act. They differ in how much detail they provide, how they collect data, and where they fit in the customer journey. For example, surveys and feedback forms reach many people and give structured data. User interviews and focus groups go deeper, letting teams ask follow-up questions and explore emotions. Social media listening and analytics watch for public complaints and trends, while prototype testing and A/B testing let teams try out changes and see what works best.
Teams often use direct feedback methods, like surveys with open-ended questions, to let customers share pain points in their own words. Sales and support teams add their own insights from daily interactions. Data analysis of key performance indicators, such as churn rate or resolution time, gives numbers that support what customers say. Combining these approaches helps teams validate findings and prioritize which pain points to address first.
Note: Sobot’s Ticketing System helps teams collect and organize feedback from many channels, making it easier to spot patterns and trends in pain point mapping.
When to Use Each Method
Choosing the right method depends on the goal, the stage of the journey, and the type of pain point. Teams can use the "Look, Ask, Try" framework to decide which method fits best:
| Research Method | Most Effective Scenario | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Look | Identifying latent needs | Best when customers may not be aware of their pain points; requires unbiased observation to understand real customer interactions with a product or service. |
| Ask | Uncovering explicit pain points and new ideas | Useful for gathering open-ended insights from customers and stakeholders through questions and interviews; helps reveal clearly identifiable challenges. |
| Try | Developing empathy through direct participation | Effective when researchers can engage in the customer's experience firsthand, such as field observation or using props to simulate scenarios, to observe real interactions and better understand needs. |
- Teams use "Look" methods, like observing customers or reviewing journey analytics, when they want to find hidden pain points. For example, watching how customers move through a website can show where they get stuck.
- "Ask" methods, such as interviews and surveys, work well when teams want to hear about pain points directly from customers or personas. These methods help uncover clear problems and gather new ideas.
- "Try" methods involve stepping into the customer’s shoes. Teams might use journey simulations or role-play to feel what customers feel. This builds empathy and helps teams understand pain points on a deeper level.
Customer journey maps and pain point mapping both benefit from using the right method at the right time. For example, teams might use surveys to gather broad feedback, then follow up with interviews to dig deeper into specific issues. Sobot’s AI solutions help automate data collection and analysis, making it easier to choose the best method for each stage of the journey.
Combining Approaches for Deeper Insights
No single method gives a complete picture of customer pain points. Teams get the best results when they combine different approaches. This mixed-methods strategy helps validate findings, uncover hidden issues, and create a more accurate map of the customer journey.
- Teams often start with qualitative interviews to hear stories and emotions, then use quantitative surveys to measure how common each pain point is.
- Sentiment analysis tools, like those in Sobot’s Ticketing System, help teams measure the emotional impact of pain points and prioritize which ones to fix first.
- Data visualizations that combine qualitative and quantitative data make it easier to see patterns and share insights across teams.
- Cross-functional teams, including product, design, engineering, and support, bring different perspectives to the analysis. This leads to richer insights and better solutions.
- Collaborative tools and regular review sessions help everyone stay aligned and focused on the most important pain points.
- Automation speeds up the process, ensures consistency, and helps teams find subtle themes that might be missed by manual analysis.
Tip: Using customer journey maps and pain point mapping together helps teams see both the big picture and the details. For example, journey maps show every step and touchpoint, while pain point mapping highlights where customers struggle most.
Teams can also use JTBD frameworks to understand what customers want to achieve at each stage of the journey. By mapping jobs, personas, and pain points together, teams create a clear strategy for improvement. Sobot’s solutions support this approach by integrating feedback from all channels, automating analysis, and providing actionable insights.
Combining methods leads to a deeper understanding of customer needs. It helps teams build empathy, make better decisions, and design solutions that truly solve customer problems. Companies that use this strategy often see higher satisfaction, lower churn, and stronger business growth.
Practical Guidance for Customer Service Teams
Choosing the Right Research Approach
Customer service teams need a clear strategy to select the best method for uncovering pain points. The right approach depends on the level of the customer journey and the type of pain point. Teams can use the following table to match identification methods and prioritization criteria to each level:
| Pain Point Level | Identification Methods | Prioritization Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Interaction Level | Usability testing | Severity of issues, frequency of occurrence, user impact |
| Journey Level | Exploratory research: user interviews, diary studies, journey mapping | Impact across the journey, feasibility of solutions |
| Relationship Level | Long-term data integration: benchmarking surveys, analytics, single customer view | Impact across multiple journeys, churn rate, brand loyalty loss |
Teams should align their research with the complexity of the customer journey. For example, usability testing works well for specific touchpoints, while journey mapping and JTBD interviews help uncover broader issues. Prioritizing pain points by severity and frequency ensures resources focus on the most impactful problems.
Implementing with Sobot Solutions
Sobot offers customer service teams a powerful set of solutions to support pain point research and resolution. Sobot’s AI-powered platform delivers 24/7 support, automates repetitive tasks, and enhances engagement across every customer journey. Teams benefit from real-time analytics and predictive modeling, which help identify friction points and optimize the journey proactively.
- Sobot integrates omnichannel communication, AI Agent, AI Copilot, and AI Insight to improve service efficiency.
- The platform automates workflows and supports personalized communication, reducing agent workload by 60%.
- Over 300 statistical reports with thousands of indicators allow deep analysis of customer data and journey trends.
- Flexible APIs enable integration with systems like Amazon, Shopify, and Salesforce, supporting a tailored strategy for each business.
- Sobot’s AI-driven JTBD analysis and journey mapping help teams pinpoint and resolve pain points quickly.
- The combination of AI and human collaboration reduces resolution time to under one minute and improves Net Promoter Score by 35%.
- Case studies from e-commerce and retail show that Sobot’s solutions lead to higher satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Tip: Sobot’s platform supports continuous improvement by providing real-time feedback and actionable insights throughout the customer journey.
Real-World Example: OPPO and Sobot
OPPO, a global smart device leader, uses Sobot’s AI-powered platform to collect and analyze customer feedback from multiple channels. The company applies JTBD and journey mapping to identify pain points, such as battery life concerns. OPPO improved product performance based on this feedback, using natural language processing and predictive analytics.
| Evidence Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Platform Used | OPPO uses Sobot to gather feedback from social media, email, and in-app surveys. |
| Pain Point Identification | Identified battery life issues through customer journey analysis. |
| Product Improvement | Enhanced battery performance in new models based on journey feedback. |
| AI Techniques Applied | Used JTBD, journey mapping, NLP, and predictive analytics. |
| Customer Retention Impact | Reduced complaints by 25% and churn rates by 30%. |
| Customer Satisfaction | Increased satisfaction by 30% through personalized support and journey orchestration. |
| Ethical AI Use | Maintains transparency and offers opt-out options for customers. |
OPPO’s results show how a focused strategy using JTBD and journey mapping, supported by Sobot’s solutions, can transform the customer journey. The company achieved fewer complaints, higher satisfaction, and improved retention by acting on real customer insights.
Effective customer pain point research drives business growth and customer satisfaction. Teams use a mix of methods—like interviews, surveys, and observation—to uncover challenges in the customer journey. Sobot’s Ticketing System and AI solutions help companies automate feedback collection, analyze data, and resolve issues quickly. By prioritizing pain points, businesses improve the customer experience and build loyalty. Next, teams should centralize communication, monitor feedback, and update support strategies. Exploring Sobot’s platform empowers organizations to deliver a seamless journey and create lasting customer relationships.
FAQ
What is a customer pain point?
A customer pain point is a specific problem or frustration that a customer faces during their experience with a business. For example, long wait times or confusing checkout steps often cause customers to leave without buying.
How do companies collect feedback about pain points?
Companies use surveys, interviews, and support tickets to gather feedback. Sobot’s Ticketing System collects messages from email, chat, and voicemail. This helps teams see common issues and respond faster.
Why is it important to fix customer pain points quickly?
Fixing pain points quickly helps keep customers happy and loyal. According to PWC, 32% of customers will stop doing business with a brand after one bad experience.
How does Sobot help businesses improve customer experience?
Sobot offers AI-powered tools that automate support, track feedback, and provide real-time analytics. These features help businesses find and solve pain points, leading to higher satisfaction and better retention.
Can pain point research help all types of businesses?
Yes, pain point research benefits many industries, including retail, e-commerce, finance, and education. Companies like OPPO use Sobot’s solutions to improve service and increase customer loyalty.
See Also
Best Voice of Customer Tools Reviewed and Analyzed
Ten Ways to Improve Customer Satisfaction Through Live Chat
Ten Guidelines for Selecting Social Media Support Software
Ways Chatbots Enhance Customer Experience in E-commerce
Effective Live Chat Techniques to Improve SaaS Customer Support
