E-commerce refers to the transaction of goods and services over the Internet, with B2B (business-to-business) and B2C (business-to-customer) as its two core models.
- B2B E-commerce: One business sells its products or services to other businesses, focusing more on long-term partnerships and bulk transactions.
- B2C E-commerce: It targets consumers directly, emphasizing immediate conversion and user experience.
These two models show significant differences in their target customers, transaction processes, and marketing strategies. The purpose of this article is to differentiate between the two models, help readers understand the core differences between B2B vs. B2C e-commerce, and provide a practical guide for practitioners.

B2B vs. B2C E-Commerce: Comparative Analysis
To succeed in starting out in these two types of e-commerce businesses, you need a deep understanding of both horizontal and vertical aspects.
First, let’s compare them horizontally to explore the difference between B2B and B2C e-commerce.
- Typical B2B e-commerce companies primarily deal in industrial goods, electronic components, machinery and equipment, wholesale agricultural products, chemical products, medical equipment, and construction materials, etc. Key players include Alibaba, Global Sources, DHgate, ThomasNet, and TradeKey, focusing on bulk purchasing and supply chain management for businesses.
- B2C e-commerce brands, on the other hand, focus on selling consumer goods such as clothing, footwear, beauty and skincare products, 3C electronics, home goods, health and nutritional supplements, audio-visual products, books, food, and beverages. Representative platforms in this sector, such as Amazon, Tmall, JD.com, eBay, Rakuten, OTTO, and Mercado Libre, target end consumers globally, emphasizing user experience, product variety, and efficient logistics.
B2B and B2C e-commerce have significant differences in target customers, sales cycles, buying behaviors, order values, transaction complexity, and customer service. These differences mean they focus on different aspects of marketing strategies, platform design, and operation management.
1. Target Audience
- B2B: Targets business clients, such as purchasing managers, professionals, and decision-makers. The customer base is narrow and specialized, typically large enterprises, SMEs, government agencies, etc. B2B e-commerce transactions focus on establishing trust, ongoing support, and long-term partnerships.
- B2C: Targets individual consumers, and the customer base is broad and diverse. Purchases are often based on personal needs, emotions, and preferences, with a significant amount of buying being impulsive.
2. Sales Cycle
- B2B: The sales cycle is lengthy, involving multiple layers of approval and numerous stakeholders. The decision-making process is complex and requires thorough research, with purchasing plans usually made in advance.
- B2C: Purchasing decisions are made quickly, typically by individual consumers independently. The sales process is simple and direct.
3. Buying Behavior
- B2B: Purchases are based on business needs, emphasize rational analysis, and are focused on ROI. Purchase frequency is relatively low, but order volumes are large. There is a strong focus on product technical specifications and custom e-commerce solutions.
- B2C: Purchases are often driven by price, convenience, and emotions. Order values are smaller, but purchase frequency is high. Products are mostly standardized and ready to
4. Order Value
- B2B: Order values are usually large due to bulk purchasing and high-value items, with prices often customized and negotiated.
- B2C: Order values are smaller, with fixed and transparent prices for all consumers.
5. Transaction Complexity
- B2B: The transaction process is complex, involving quote management, credit limit approval, multi-account management, customized quotes, contract terms, etc.
- B2C: The transaction process is simple, with diverse and instant payment options, supporting quick check-out and promotional offers.
6. Product Complexity and Catalog Management
- B2B: Products are highly technical, meeting specific business needs. Product catalogs and prices are customized based on customer groups, emphasizing personalization and professionalism.
- B2C: Products are mostly standardized with a unified catalog, emphasizing user experience and ease of use.
7. Customer Service Requirements
- B2B: Requires around-the-clock professional customer service to support complex technical inquiries and order management. It emphasizes maintaining long-term customer relationships.
- B2C: Customer service mainly handles common issues like returns, exchanges, and order inquiries, with more support for automation and self-service options.
| Dimension | B2B E-Commerce | B2C E-Commerce |
| Target Audience | Business clients (e.g., manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers) | Individual consumers |
| Sales Cycle | Long (multi-layered decisions and approvals) | Short (quick consumer decisions) |
| Buying Decision | Based on business needs and rational analysis | Driven by emotions and personal preferences |
| Order Value | High (bulk purchasing or solution) | Low (small-order values) |
| Transaction Complexity | High (price negotiations, custom demands, complex contracts) | Low (transparent prices, simple processes) |
| Website Design Focus | Solutions, technical specs, comparison charts, sales support | Product visuals, user experience, promotions |
| Marketing Content Style | Data-driven, professional | Emotion-driven, creative, and engaging |
B2B vs. B2C E-Commerce: Market Status (2025 Latest)
In the second step, we move on to the respective market situation for longitudinal data acquisition.
Only by doing a good job in market insight and trend prediction, and adapting to market changes, can we take the lead in industry competition and cooperation.
Both the B2B and B2C e-commerce markets are growing rapidly, but their growth drivers and market characteristics differ.
B2B E-Commerce Market
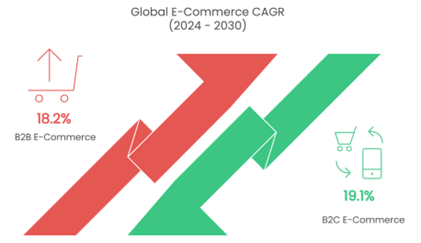
- The global B2B e-commerce market size was estimated at USD 18,665.95 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.2% from 2024 to 2030.
- Rapid technological advancements, such as AI, machine learning, and data analytics, are crucial for the expansion of the B2B market. These technologies enable businesses to offer personalized customer experiences, predictive analytics, and process automation, thereby improving productivity and competitiveness.
- The adoption of B2B e-commerce is driven by its automatic integration with enterprise systems such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), automated order processing, supply chain visibility, and (Customer Relationship Management) CRM.
- The North American market accounted for approximately 40% of the market share in 2023. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness significant growth, mainly due to the widespread use of digital technologies and the development of medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
B2C Market
- The global B2C e-commerce market size was estimated at USD 5.47 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 19.1% from 2024 to 2030.
- Interactive product visualization, virtual try-ons, personalized recommendations, and targeted promotions significantly enhance customer engagement and loyalty.
- The integration of social media and the rise of influencer culture have greatly boosted the growth of the B2C market.
- The Asia-Pacific region accounted for approximately 58% of the market share in 2023 and is expected to continue its rapid development, mainly due to the widespread use of smartphones, digital payments, and e-commerce platforms.
From the data analysis above, both North America and the Asia-Pacific region hold significant positions in the two markets. Companies should consider devising strategies for these regions to leverage their growth potential. Moreover, as market saturation increases and competition becomes more intense, businesses in both B2B and B2C markets need to think about adopting new technologies to boost efficiency and enhance the customer experience.
B2B vs. B2C E-Commerce: Marketing Funnels, Sales Funnels, and Commonalities
The third step is where a significant difference can be made and is also the aspect of marketing and management that all decision-makers should focus on the most.
All marketing funnels are essentially refined based on the AIDA model, which consists of 4 stages—Awareness, Interest, Desire, and Action.
Therefore, when it comes to B2B and B2C marketing funnels, their operational logic is almost entirely the same. However, there are some differences at the stage level. This means that while the final marketing strategies may diverge in certain aspects, they also share underlying commonalities.
B2B vs. B2C E-Commerce Marketing Funnel
| Marketing Funnel Stage | B2B E-Commerce Marketing Funnel | B2B E-Commerce Marketing Funnel |
| Awareness | >B2B brands aim to attract potential customers who are seeking business solutions. >They can also draw in corporate clients through industry reports, whitepapers, and seminars. |
>B2C brands, on the other hand, focus on making customers aware of their products.
>They primarily attract consumers through advertising, social media, and influencer marketing. |
| The Common Factor: Both aim to capture the attention of their target customers and make them aware of the brand and its products. | ||
| Interest | >B2B brands may offer detailed product brochures, case studies, and free trials. | >B2C brands may spark interest through coupons, pop-ups, and product images. |
| The Common Factor: Both aim to engage the customer and encourage a deeper exploration of the product or service. | ||
| Desire | >B2B brands emphasize how their products meet business needs and offer customized solutions.
>Most B2B brands showcase recommendations from existing customers, success stories, and reviews from third-party websites. |
>B2C brands, however, tend to evoke the desire to purchase through emotional appeals and promotional activities.
>Customer reviews are equally important. |
| The Common Factor: Both aim to further cultivate the customer’s desire to purchase, convincing them that the product can meet their needs or bring benefits. | ||
| Action | >Provide quotes and contract terms, and arrange for sales representatives to follow up.
>B2B brands may use payment methods such as bank transfers or wire transfers. |
>Offer convenient payment methods and fast delivery services. >Upselling and cross-selling strategies are more common in B2C businesses. |
| The Common Factor: It is crucial to implement customer retention strategies. | ||
B2B vs. B2C E-Commerce Sales Funnel
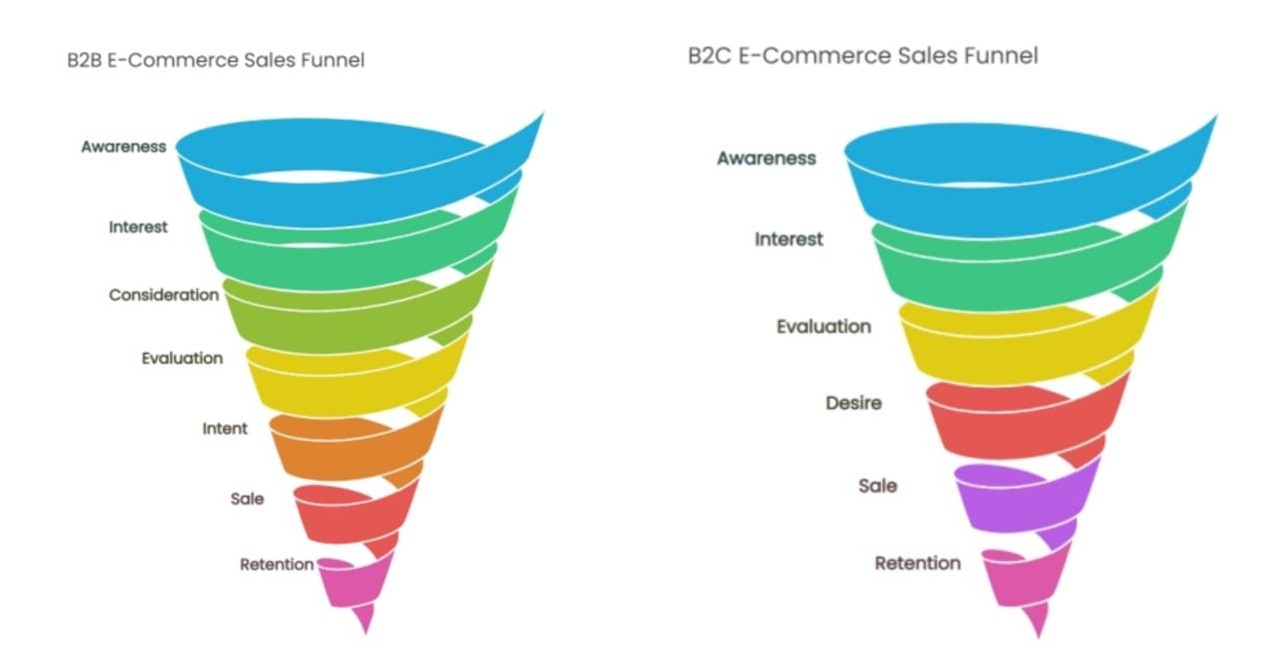
The B2B sales funnel can have up to seven stages. A clear distinction from the B2C funnel is that the “Interest” stage does not typically exist in B2C. In this stage, B2B customers usually contact the sales team or express their purchase intent through a demo request.
What are the Underlying Optimization Strategies?
From the data and marketing analysis, we see that [faster, more personalized customer issue resolution and engagement] are areas we can continuously invest and optimize in both B2B and B2C e-commerce.
For B2C brands like Samsung, OPPO, Uniqlo, Shein, MICHAEL KORS, and Tineco, customer service is key to enhancing user experience and loyalty. Consumers prefer self-service options such as dynamic FAQs and AI chatbots for quick information and reduced wait times. Samsung partnered with Sobot (customer service solution provider) to integrate a multichannel customer service platform, achieving data interoperability and intelligent support. This led to a 97% customer satisfaction rate and a 30% improvement in service efficiency.
While B2B e-commerce is more complex and buyer needs differ from B2C, this doesn’t mean B2B buyers expect lower service levels. Personalization, a boon for B2C, can also benefit B2B. B2B firms should seize every chance to connect with their target audience.
Reliable customer service center software can meet these optimization needs. As the bridge between businesses and customers, a customer service center is essential in both B2B and B2C for an efficient, intelligent support system. So, what are their logic and techniques for enhancing the e-commerce experience?
1. Omnichannel Experience
Modern customers interact with businesses through various channels. A reliable customer service center can integrate and manage these channels seamlessly, ensuring timely and consistent responses.
2. AI Technology
AI provides 24/7 support, handling common issues to free up human agents for complex tasks. It also predicts customer needs, offers personalized recommendations, and performs sentiment analysis to proactively address issues.
More knowledge about AI in customer service support can also be found in articles: What is Generative AI for Customer Service?
AI in Retail – 7 Strategies to Boost E-commerce Conversion Rate Growth
3. Data-Driven Optimization
Advanced customer service software integrates data analytics to monitor inquiries, response times, and feedback. This helps businesses gain insights into customer needs and continuously improve service processes, knowledge bases, and training.
4. Automation and Process Management
Automation tools like ticket auto-assignment and SLA-based time-management standardize workflows, reduce errors, and improve response and resolution times. This not only boosts efficiency but also ensures timely follow-up and closed-loop issue management, enhancing customer trust.
Sobot: Customer Service Support is Where We Excel
Customer service support is our core strength. We specialize in creating intelligent, efficient, and comprehensive customer service solutions for all businesses, including different forms of e-commerce. Our solutions enable seamless 24/7 communication, unified multichannel management, and smart automation. Whether it’s complex custom e-commerce solutions for B2B or diverse user experiences for B2C, Sobot can provide professional support to enhance customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. We will demonstrate the advantages of e-commerce and help different forms of e-commerce to stand out in a competitive market.
In B2C e-commerce, SHEIN, J&T Express, OPPO, Weee!, OPay, Transsion, MICHAEL KORS, Samsung, Agilent, Luckin Coffee, DFS, Renogy, PalmPay, Mico are all loyal customers of Sobot.
In B2B e-commerce, we also have close cooperation with Made-in-China.com, HSG Laser, Unikey Electronics, RITH LIMITED, Sibio, PANTUM, Siemens Energy, and Bodor Laser.
Get a free demo and start your path to e-commerce success now.
FAQs
1. What role does a customer contact center fulfill in B2B and B2C e-commerce?
The customer contact center handles inquiries, manages orders, and ensures smooth transactions. In B2B, it provides technical support and customized services for complex purchasing and approvals. In B2C, it focuses on quick responses to enhance user experience and loyalty. Additionally, the customer contact center can collect customer feedback and behavioral data, providing valuable insights for companies to optimize their products and services. Feel free to contact Sobot for more demo information.
2. What is the difference between customer retention strategies for B2B and B2C e-commerce?
B2B customer retention focuses on building long-term, stable partnerships, emphasizing trust, transparent communication, and personalized services. Common strategies include account management, customized marketing, and loyalty programs.
B2C customer retention relies more on promotions, membership systems, and personalized recommendations to quickly meet consumers’ individual needs and enhance shopping experiences, driving repeat purchases.
3. Why is B2B e-commerce more complex than B2C e-commerce?
B2B customers have high demands for product specs, custom services, and after-sales support, needing professional customer and technical teams. B2C transactions are simpler, with transparent pricing and a focus on convenient, fast user experiences, backed by mature technology.
Moreover, B2B buyers handle high-value deals and consult multiple departments before purchasing, so errors are costly. B2C consumers make personal decisions, where purchase mistakes have less impact.