Introduction
As businesses strive to offer more intelligent and efficient customer experiences, AI-driven technologies like chatbots and AI agents are at the forefront. While both serve in automating interactions, AI agents go far beyond traditional chatbot capabilities—bringing autonomy, advanced reasoning, and multi-step decision-making into customer service.
This article explores the fundamental differences between chatbots and AI agents, helping businesses understand when to deploy each and how AI agents—such as those offered by Sobot—are transforming support ecosystems.
What Is a Chatbot?
Chatbots are rule-based or NLP-based programs that simulate human dialogue to provide instant responses. They rely on predefined scripts or trained intent models to answer FAQs, direct users, or trigger simple actions. These tools are valuable for handling repetitive or predictable queries and can function via text or voice.
Importantly, chatbots do not manage knowledge bases themselves—these are structured and maintained by human agents. Chatbots merely fetch and display information as configured.
They are widely adopted in customer service to handle high volumes of low-complexity interactions. The ability to provide 24/7 support without human intervention makes them cost-effective and scalable in many industries, including e-commerce, telecom, and banking.
Functionality of a Chatbot
Chatbots operate by interpreting user inputs, matching them against predefined patterns or NLP intents, and delivering corresponding responses. This process often involves identifying keywords, mapping them to known intents, and selecting appropriate responses.
Chatbots can be integrated with customer relationship management (CRM) systems, live chat software, or messaging platforms like WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and Slack. They can trigger predefined workflows—such as form submissions, ticket creation, or product recommendations—based on the detected intent.
Though they offer fast and consistent answers, they usually can’t handle ambiguous or complex queries unless extensively trained or designed with fallback logic to escalate issues.
Limitations of Chatbots
While chatbots provide value in structured scenarios, they face several limitations:
- Limited Context Awareness & Script Dependency: Chatbots often struggle to understand the broader context of multi-turn conversations and are confined by their scripted logic. If the user deviates from expected input patterns, they fail to respond accurately.
- Lack of Autonomy: They cannot take proactive actions or adapt dynamically. Chatbots are not built to handle end-to-end workflows involving real-time decision-making.
- Static Learning: Most chatbots require manual retraining and do not improve automatically over time. They lack reinforcement learning capabilities.
- No Cross-Session Memory: Unless specifically engineered with session tracking, chatbots do not remember past interactions, limiting their personalization potential.
These constraints make chatbots ideal for routine interactions but insufficient for complex or evolving tasks.
What Is an AI Agent?
AI agents are autonomous systems capable of perceiving their environment, making decisions, and taking actions to achieve specific goals. They utilize advanced machine learning models, including deep neural networks and reinforcement learning, to operate independently.
Sobot’s AI Agent is designed specifically for customer service automation, offering features like intelligent conversation handling, voice calling, and deep contextual understanding to deliver more human-like and efficient support experiences.
Functionality
AI agents can analyze large datasets, learn from interactions, and adapt to changing conditions. In customer service, this means understanding customer intent, making proactive decisions, and resolving issues without human intervention. For instance, Sobot’s AI Agent can handle a return request, verify a customer’s account, update the shipping address, and send confirmation—all within the same conversation. This capability enhances response speed, reduces workload on human agents, and ensures consistent service delivery.
AI Agent Capabilities in Customer Service
AI agents offer several advanced capabilities that make them superior to traditional bots:
- Autonomous Task Execution: They can complete multi-step actions such as resolving returns, verifying user identity, updating accounts, or issuing refunds.
- Contextual Understanding: AI agents understand conversation flow, refer back to earlier points, and maintain awareness across long exchanges.
- Proactive Decision-Making: Rather than waiting for input, they can suggest actions, remind users, or flag potential issues proactively.
- Multi-Modal Perception: They can ingest structured and unstructured data from different channels (text, API inputs, etc.) to inform decisions.
- Learning and Optimization: Through reinforcement learning and historical data analysis, AI agents continue to refine their behavior.
These capabilities enable enterprises to scale high-touch, personalized service without increasing human overhead.
Example of AI Agent in Action
Sobot’s AI Agent is designed for real-world customer service challenges. For example, in an e-commerce scenario, a customer might say:
“I want to return one item from my last order but keep the others. Also, please update my address for future orders.”
Instead of handing off to a human agent, the AI Agent can retrieve the customer’s order history, process the partial return, initiate a refund, update the delivery address, and provide confirmation—all in a single conversation, without human involvement.
This end-to-end autonomy showcases the power and efficiency AI agents bring to customer service operations.
Key Differences Between Chatbots and AI Agents
AI chatbots and AI agents both leverage artificial intelligence to support users and businesses in completing tasks, answering questions, and streamlining operations. At their core, they interact with users through text or voice, processing inputs to deliver helpful responses or take action—essentially functioning as smart digital assistants.
While they share similarities in their use of natural language processing and conversational interfaces, the terms are often mistakenly used interchangeably. This confusion arises as chatbots grow more advanced and AI agents become increasingly conversational.
However, despite their overlapping functions, these two technologies differ significantly in terms of capability, autonomy, and purpose.
Let’s break down these differences across key aspects to better understand what sets them apart.
| Aspect | Chatbots | AI Agents |
| Decision-Making | Rule-based, follows predefined scripts | Autonomous, makes data-driven decisions |
| Contextual Understanding | Basic keyword recognition | Deep NLP capabilities with contextual awareness |
| Task Complexity | Handles simple, repetitive tasks | Manages complex, multi-step processes |
| Learning & Adaptability | Limited learning, requires manual updates | Continuously learns and improves from interactions |
| User Interaction | Reactive to user inputs | Proactive and goal-oriented |
| Integration | Can integrate with external systems, but often requires configuration | Seamlessly integrates and operates across multiple systems and workflows |
| Autonomy | Needs human intervention for complex tasks | Functions independently with minimal oversight |
| Response Personalization | Static and often generic | Dynamic and tailored based on user data |
1. Decision-Making
Chatbots operate based on predefined rules and decision trees. They follow scripted paths, responding to inputs with set answers or a limited range of responses. Their actions are predictable, making them suitable for repetitive queries. However, they lack the intelligence to handle exceptions or unique scenarios. AI agents, in contrast, use algorithms to make real-time, data-driven decisions independently.
2. Contextual Understanding
Most chatbots rely on basic keyword recognition, which limits their ability to understand user intent beyond the surface level. They might misinterpret queries that are vague, indirect, or nuanced. AI agents are equipped with advanced natural language processing (NLP) capabilities, allowing them to grasp context, semantics, and conversational flow. This enables them to hold more natural, human-like conversations. They can understand sentiment, slang, and even adapt tone accordingly.
3. Task Complexity
Chatbots are ideal for handling simple, repetitive tasks like booking appointments, checking order statuses, or answering FAQs. Their performance drops when dealing with multi-step or logic-heavy queries. On the other hand, AI agents can process large volumes of data and manage complex workflows across departments. They can coordinate between various systems, handle multiple objectives simultaneously, and make decisions accordingly. This makes them highly effective for enterprise-level automation and support.
4. Learning and Adaptability
Traditional chatbots don’t learn on their own– they need human intervention to expand or update their knowledge base. This means they become outdated unless developers manually feed new data. In contrast, AI agents continuously learn from every interaction using machine learning algorithms. They evolve over time, adapting to user behavior, changing conditions, and new data inputs. This allows them to improve accuracy, efficiency, and contextual handling with minimal oversight.
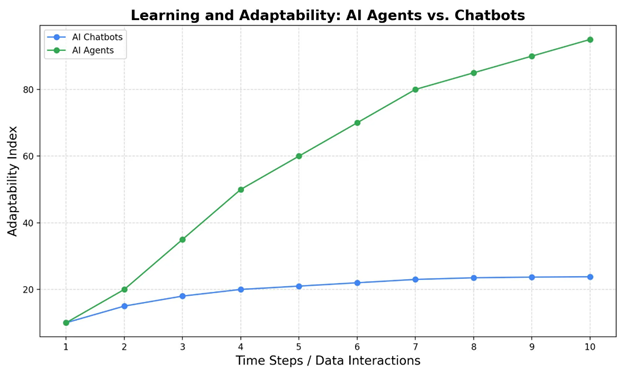
5. User Interaction
Chatbots are reactive tools; they wait for a user to initiate a conversation and respond accordingly. They are not capable of predicting needs or guiding users proactively. AI agents, however, can do both — respond to user input and take initiative based on predefined goals or real-time analysis. For example, an AI agent can remind a user of a missed task or offer help based on behavior patterns. This proactive engagement greatly enhances user experience and productivity.
6. Integration
Chatbots are typically integrated into a single platform like a website or messaging app, and they rarely function beyond their host environment. They often need third-party plugins or custom coding to connect with other tools. In contrast, AI agents are built for deep integration across multiple platforms, tools, and data sources. They can communicate with CRM systems, ERP tools, and even IoT devices. This enables them to execute more complex and cross-functional tasks.
7. Autonomy
Chatbots depend heavily on human supervision when it comes to handling new or complex queries. If a conversation deviates from the script, the chatbot either fails or escalates to a human. AI agents operate with a high level of autonomy. They analyze situations, learn from outcomes, and take appropriate actions without needing constant human input. This independence makes them suitable for mission-critical environments like healthcare, finance, and logistics.
8. Response Personalization
Most chatbots provide generalized responses that apply to a broad audience, lacking personal touch. Even with some personalization, it’s usually based on limited, surface-level data like a name or location. AI agents go further by analyzing historical user data, preferences, behavior patterns, and even tone of voice. This allows them to generate highly relevant and personalized responses. The result is a more engaging and tailored user experience.
Use Cases and Applications
To illustrate the real-world roles of chatbots and AI agents, here’s a side-by-side comparison of how each is typically applied across various industries:
| Industry | Chatbot Applications | AI Agent Applications |
| E-commerce | Respond to basic product queries, assist in order tracking, provide promotions info | Handle returns/exchanges, modify orders, recommend products, resolve delivery issues proactively |
| Customer Service | Answer FAQs, route queries to departments | Autonomously complete refund processes, account changes, user verification, complaint resolution |
| Finance | Provide balance inquiries, credit card info, interest rates | Offer financial planning suggestions, detect fraud, evaluate risk, process complex transactions |
| Healthcare | Book appointments, provide basic symptom checker | Deliver personalized health guidance, monitor patient preferences, follow up on treatments |
| Telecom | Show plan details, check usage, help with bill inquiries | Diagnose service problems, recommend plans, handle SIM activations and upgrades |
| Travel | Provide booking confirmation, basic destination info | Change travel itineraries, automate cancellations or rebookings, suggest dynamic travel packages |
| Education | Share course info, help with admissions queries | Assist with student enrollment, track progress, offer personalized learning suggestions |
| Retail | Provide store hours, product availability, and location info | Manage returns, track loyalty benefits, notify customers of restocks or new launches |
How to Choose Between a Chatbot and an AI Agent
Choosing between an AI chatbot and an AI agent depends on your specific needs, budget, complexity of tasks, and future goals. Both tools serve valuable purposes, but they operate at different levels of intelligence and autonomy. Here’s how they compare across the key decision-making factors:
1. Intended Use Case
Chatbot: Best suited for simple, repetitive tasks such as answering frequently asked questions, collecting basic user data, or guiding customers through pre-defined processes. They work well in customer support, basic lead generation, and onboarding scenarios.
AI Agent: Ideal for handling complex tasks that require understanding context, making decisions, and executing multi-step workflows. They’re great for use cases like automated troubleshooting, dynamic sales support, and personalized recommendations across multiple channels.
2. Budget Considerations
Chatbot: Generally more cost-effective to build, deploy, and maintain. Perfect for businesses with tight budgets that still want to provide automated support or assistance without investing in advanced AI infrastructure.
AI Agent: Requires a larger investment due to its sophisticated architecture and advanced capabilities. Higher upfront and ongoing costs are expected, but they can deliver a strong ROI for businesses with complex needs and higher operational demands.
3. Technical Resources and Maintenance
Chatbot: Can be developed and managed with minimal technical skills. Most chatbot platforms offer user-friendly interfaces and templates that reduce the need for in-depth coding or machine learning expertise.
AI Agent: Demands a team with technical expertise in AI, natural language processing, machine learning, and systems integration. Also requires continuous training, performance monitoring, and updates to remain effective and accurate.
4. Scalability and Future Growth
Chatbot: Can handle large volumes of basic interactions efficiently but struggles to adapt to dynamic scenarios or evolving user needs. Limited in terms of scalability for advanced use cases.
AI Agent: Designed for adaptability and growth. AI agents can scale across departments, integrate with various platforms, and evolve as your business processes and user expectations become more complex.
Conclusion
While chatbots have laid the foundation for automated interactions, AI agents represent the next evolution—bringing intelligence, flexibility, and true task autonomy to digital service experiences.
Chatbots are effective for predictable, low-touch scenarios. However, businesses seeking intelligent, proactive, and context-rich automation should consider AI agents. Platforms like Sobot lead this transformation, helping companies move beyond reactive support to fully autonomous assistance.
In the future, hybrid systems will combine both technologies—chatbots handling simple cases, while AI agents manage complex ones. For organizations aiming to stay competitive, now is the time to embrace this shift.
FAQs
What’s the difference between Chatbot and AI Agent?
Chatbot and AI Agent are very similar, the biggest difference lies in interaction way.
Chatbot: Interact with customers through the chat interface in text or voice.
AI Agent: Except for chat, AI Agent can also provide service to customers in voice, email or other ways.
Sobot Chatbot has a history of over 10 years and has been trusted by tens of thousands of businesses, so it has already become a mature product.
With the popularity of ChatGPT, AI Agent often represents chatbot with LLM technology, better information processing capacity and more powerful logic. Therefore, Sobot Chatbot has also leveraged the latest LLM technology to be more intelligent.
If your businesses need intelligent service, please feel free to contact us. We can provide various AI customer contact products like Chatbot , Voicebot , AI Agent, AI Copilot and more.
How is AI technology applied to Sobot contact center solution?
There are many AI applications in Sobot contact center solution.
1. For different roles: AI agents can receive customers, naturally communicate with them to solve common problems; AI Copilot assists agents in improving efficiency; AI Insight supports administrators to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the overall business, customer concerns, and team status.
2. For different contact ways: There are AI chatbot in online chat, and AI voicebot in calling.
For more specific functions, please feel free to contact us for a detailed understanding.
Does Sobot provide free AI Chatbot, AI Voicebot and AI Agent?
Sobot AI solution is mainly for enterprises needs payment under most situations.
But if you are a global public welfare organization that needs to use Sobot products in public health and safety, we will provide them to you for free.
Sobot products have no minimum seat number or conversation consumption limits, so if you’re a startup or small-sized team, it’s cost-effective to contact us. We can provide a free trial to you!