What is Voice Extensible Markup Language VXML

Voice extensible markup language (VXML) serves as a standard for building voice-based applications, enabling seamless communication between humans and machines. It powers technologies like interactive voice response (IVR) systems, which rely on tools such as automatic speech recognition (ASR) and text-to-speech (TTS) to interpret and respond to user inputs. These systems also utilize natural language processing (NLP) for contextual understanding, enhancing user experiences. Businesses like Sobot leverage VXML to create efficient solutions for customer service, ensuring faster query resolution and improved satisfaction. This technology has become indispensable in modern call centers, streamlining operations and fostering accessibility.
Understanding Voice Extensible Markup Language (VXML)
What is VoiceXML?
Definition and purpose of VoiceXML
VoiceXML, short for Voice Extensible Markup Language, is a web-based standard designed specifically for creating voice-driven applications. It enables you to develop interactive voice response (IVR) systems that allow users to interact with technology through spoken commands or keypad inputs. By focusing on business logic rather than telephony complexities, VoiceXML simplifies the development process for voice applications. This makes it an essential tool for businesses aiming to enhance customer experiences through automated voice interactions.
Comparison to HTML and other markup languages
VoiceXML shares similarities with HTML but serves a different purpose. While HTML is used to create visual web pages, VoiceXML focuses on audio-based interactions. Here's a quick comparison:
| Feature | VoiceXML | HTML |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Designed for voice applications | Designed for visual web pages |
| Input/Output | Handles audio input and output | Focuses on visual presentation |
| Interaction Type | Facilitates human-computer dialogs over phone | User interaction through graphical elements |

VoiceXML also stands out among other markup languages due to its platform independence and flexibility. You can reuse VoiceXML scripts across various IVR systems, modify them easily, and integrate them with web applications or APIs. This adaptability makes it a preferred choice for businesses like Sobot, which leverage VoiceXML to power their intelligent IVR systems and AI-driven voicebots.
History and Evolution
Origins and development of VoiceXML
The development of VoiceXML began in March 1999 when AT&T, IBM, Lucent, and Motorola formed the VoiceXML Forum. This collaboration aimed to create a standardized language for voice applications. By September 1999, the Forum released VoiceXML 0.9 for member review, and in March 2000, VoiceXML 1.0 was officially published. Over the years, updates like VoiceXML 2.0 and 2.1 introduced new features based on user feedback, solidifying its role as a leading standard for voice-driven technologies.
Role of the VoiceXML Forum and W3C in standardization
The VoiceXML Forum played a pivotal role in promoting the adoption of VoiceXML. It certified platforms and developers, collaborated with standards organizations, and published best practices. In May 2000, the Forum submitted VoiceXML 1.0 to the W3C’s Voice Browser Working Group, which adopted it as the foundation for a W3C dialog markup language. This collaboration ensured that VoiceXML remained a widely accepted standard, enabling businesses to build robust voice applications that integrate seamlessly with web technologies.
The Purpose and Importance of VoiceXML in IVR Systems
Why VoiceXML is Essential
Enabling voice-driven applications
Voice extensible markup language (VXML) plays a crucial role in enabling voice-driven applications. It provides unparalleled portability, allowing applications to run on any compliant platform. This eliminates vendor lock-in and ensures flexibility for businesses. Similar to HTML, VoiceXML simplifies the development of IVR systems by leveraging existing web technologies. Developers can use familiar tools to create powerful speech-driven applications without needing specialized telephony knowledge. Additionally, VoiceXML integrates seamlessly with corporate databases via web servers, enabling real-time access to information. This capability saves time and reduces costs, making it an essential tool for businesses aiming to enhance their customer service operations.
Enhancing customer service experiences

VoiceXML enhances customer service experiences by enabling efficient and accessible interactions. It allows users to interact with IVR systems through voice commands, making services more inclusive for individuals who face challenges with text-based interfaces. Furthermore, VoiceXML supports the development of flexible and dynamic IVR applications that can handle high call volumes while maintaining service quality. For example, Sobot’s intelligent IVR system, powered by VoiceXML, offers features like smart call routing and multilingual support. These features ensure that customers receive personalized assistance, improving satisfaction and reducing resolution times.
Benefits of VoiceXML in Call Centers
Simplifying IVR system development
VoiceXML simplifies IVR system development by utilizing existing web technologies. Developers can connect IVR systems directly to corporate databases, enabling seamless access to stored information. This reduces development time and costs while allowing businesses to leverage their current technology investments. The portability of VoiceXML applications across platforms further enhances flexibility, enabling businesses to choose the best solutions without being tied to specific vendors.
Improving accessibility for diverse users
VoiceXML improves accessibility by enabling voice-based interactions over the phone. This feature is particularly beneficial for users who may struggle with traditional text-based interfaces. The simplicity of VoiceXML development allows businesses to create applications tailored to various user needs. For instance, Sobot’s IVR systems offer multilingual support and time zone settings, ensuring that diverse customer groups receive efficient and personalized service.
Reducing operational costs and increasing efficiency
VoiceXML reduces operational costs by supporting standard hardware and scalable solutions. Businesses can use existing equipment and scale their systems cost-effectively as their needs grow. For example, separating application logic from telephony equipment allows for affordable scaling. Additionally, competition among developers ensures a variety of cost-effective IVR solutions. Sobot’s Voice/Call Center leverages these benefits to provide businesses with a stable and efficient communication platform, helping them reduce costs while enhancing customer interactions.
Key Components and Features of VoiceXML
Core Elements of VoiceXML
Sessions, applications, and documents
Voice extensible markup language (VXML) relies on several core elements to create seamless voice-driven applications. Sessions manage the interaction between users and the system, ensuring continuity during calls. Applications define the logic and functionality of the voice system, while documents specify the interaction dialogs and handle user inputs. These elements work together to deliver a smooth experience. For example, a VoiceXML document might include prompts to guide users through a menu or form, while the application processes their responses. Platforms like Sobot’s Voice/Call Center utilize these elements to build intelligent IVR systems that enhance customer service efficiency.
Menus, forms, and prompts
Menus, forms, and prompts are essential components that structure user interactions in VoiceXML applications.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Menu | Presents options for users and transitions based on their selection. |
| Form | Collects values for fields, specifies prompts, and evaluates user input. |
| Prompt | Guides users by specifying expected input for each field. |
These components ensure clarity and ease of use. For instance, prompts in Sobot’s IVR systems help users navigate multilingual menus, improving accessibility and satisfaction.
Supporting Features
Grammars for speech recognition
Grammars enhance speech recognition by defining specific words and phrases for user prompts. This feature enables robust speaker-independent recognition, making VoiceXML applications more reliable. For example, Speech Recognition Grammar Specification (SRGS) supports both spoken and DTMF inputs, ensuring functionality in noisy environments. Confidence levels reported by speech recognizers allow systems to offer alternatives when uncertain. You can see this in action with Sobot’s AI-powered Voicebot, which uses grammars to deliver accurate and efficient interactions.
Variables and events for dynamic interactions
VoiceXML uses variables and events to create dynamic and responsive applications. Variables store user inputs, while events trigger actions based on specific conditions. This flexibility allows you to design systems that adapt to user needs in real time. For instance, Sobot’s IVR systems leverage these features to provide personalized experiences, such as routing calls based on user preferences or time zones.
Error handling and user-friendly prompts
Error handling ensures smooth interactions by addressing issues like misrecognition or invalid inputs. VoiceXML applications use prompts to guide users back on track, minimizing frustration. For example, if a user provides an incorrect response, the system might offer a clarification prompt to resolve the issue. Sobot’s IVR systems excel in this area, offering multilingual and context-aware prompts that enhance user satisfaction.
How VoiceXML Works in Practice
VoiceXML Infrastructure
Role of voice browsers and telephony systems
Voice browsers and telephony systems form the backbone of voice extensible markup language (VXML) applications. A voice browser acts like a web browser but interprets VXML instead of HTML. It connects callers to voice applications by managing communication between the user and the application server. For example, when you call a customer service hotline, the voice browser retrieves VXML documents from the server and processes them to guide your interaction. Telephony systems, on the other hand, handle the connection to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), enabling voice communication. Together, these components ensure smooth interactions, whether you're checking your bank balance or booking a flight. Companies like Delta Airlines use this setup to provide services such as flight status updates, showcasing how voice browsers and telephony systems work in harmony.
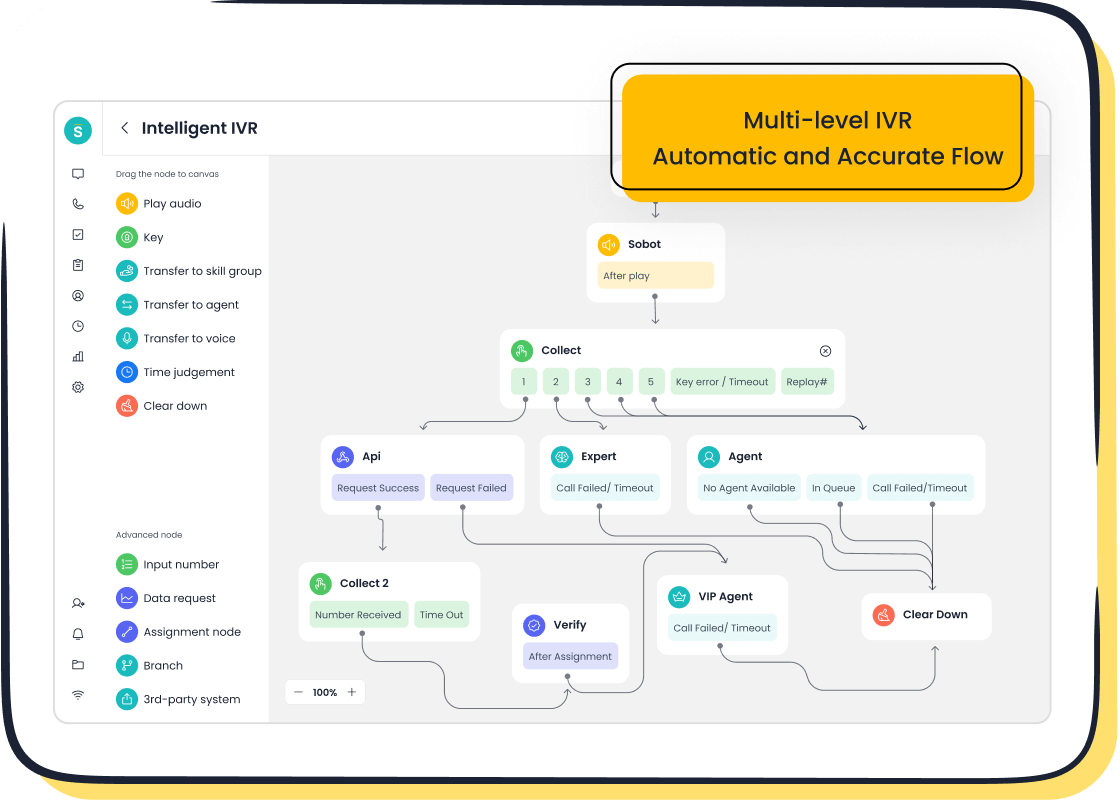
Integration with platforms like Sobot's Voice/Call Center
Platforms like Sobot's Voice/Call Center seamlessly integrate with VXML infrastructure to enhance customer service. Sobot's solution combines intelligent IVR, AI-powered voicebots, and telephony systems to deliver efficient and personalized interactions. For instance, its smart call routing feature ensures that your call reaches the right agent or department. Additionally, Sobot's platform supports global telephony, enabling businesses to serve customers worldwide. This integration not only improves accessibility but also reduces operational costs, making it a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes.
Process Flow of VoiceXML
How VoiceXML documents are interpreted
The interpretation of VoiceXML documents follows a structured process:
- The system selects a form item based on predefined conditions.
- Prompts guide you to provide input, such as speaking a command or pressing a key.
- Your input is collected and processed, filling fields or triggering specific actions.
- The system executes actions related to the filled fields, such as retrieving data.
- The process concludes when the system transfers control or completes all tasks.
This flow ensures that your interaction is smooth and efficient. For example, when you call a supermarket's IVR system to check order status, the prompts and responses follow this sequence to provide accurate information.
User interaction through voice or keypad inputs
VoiceXML applications allow you to interact using either voice or keypad inputs. When prompted, you can respond by speaking commands like "Check balance" or pressing corresponding keys on your phone. The system uses speech recognition software to process spoken inputs and DTMF tones for keypad entries. This dual-input capability ensures accessibility for diverse users. For instance, Sobot's IVR systems leverage this feature to handle high call volumes while maintaining accuracy, making it easier for you to get the help you need.
Applications and Benefits of VoiceXML in Customer Service
Real-World Use Cases
IVR systems in industries like banking and healthcare
Voice extensible markup language (VXML) has transformed customer service across industries by enabling efficient IVR systems. In banking, it powers automated customer service, allowing you to check balances or transfer funds through voice commands. Healthcare providers use it for patient communications, such as appointment reminders or prescription refills. Other common applications include order inquiries, package tracking, and emergency notifications.
| Industry | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Banking | Automated customer service |
| Healthcare | Patient communications |
| General | Order inquiry, package tracking |
| General | Emergency notification |
| General | Prescription refilling |
| General | Voice access to email |
These examples highlight how VXML simplifies interactions, making services more accessible and efficient for users.
Voice-enabled virtual assistants and customer support automation
Voice-enabled virtual assistants leverage VXML to automate customer support. You benefit from unparalleled portability, as these applications run on any platform without vendor restrictions. The development process mirrors HTML, making it straightforward to create and modify applications. Integration with existing business systems enhances service delivery, while reduced hardware needs lower costs. For example, Sobot’s AI-powered Voicebot uses VXML to deliver intelligent, real-time interactions, ensuring seamless customer experiences.
Advantages for Businesses
Streamlining call center operations with Sobot's Voice/Call Center
VXML streamlines call center operations by enabling flexible application development and deployment. Sobot’s Voice/Call Center integrates VXML with smart call routing and multilingual support, ensuring your calls reach the right agent. Its global telephony capabilities allow businesses to serve customers worldwide, reducing operational costs while maintaining high service quality.
Enhancing self-service options for customers
VXML enhances self-service options by integrating with business applications and data. This allows you to access information or complete tasks without agent assistance. Sobot’s IVR systems, for instance, offer customizable menus and multilingual prompts, ensuring you receive efficient service tailored to your needs.
Improving customer satisfaction and reducing resolution times
VXML improves satisfaction by enabling faster query resolution. Features like dynamic prompts and error handling ensure smooth interactions. Sobot’s solutions, such as its intelligent IVR, reduce resolution times by 50%, as seen in the success story of Weee!, where customer satisfaction reached 96%.
Voice extensible markup language (VXML) has revolutionized how businesses interact with customers by enabling voice-driven applications. It simplifies IVR development, enhances accessibility, and integrates seamlessly with existing systems. These features make it a cornerstone of modern customer service, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
For example, VXML's unparalleled portability allows applications to run on any platform, eliminating vendor lock-in. Its flexible development process, similar to HTML, ensures faster deployment and easy modifications. Businesses also benefit from reduced hardware costs and scalable solutions, making VXML a cost-effective choice.
Sobot's Voice/Call Center exemplifies the power of VXML. With intelligent IVR, AI-powered voicebots, and global telephony support, it delivers personalized and efficient customer experiences. By leveraging VXML, Sobot helps businesses streamline operations, enhance self-service options, and achieve higher customer satisfaction.
FAQ
What is a VXML document, and why is it important?
A VXML document is a file that defines the structure and flow of a voice application. It contains instructions for prompts, responses, and user interactions. This document ensures a seamless voice conversation flow by guiding the system on how to handle inputs and deliver outputs effectively.
How does VXML enhance IVR systems?
VXML simplifies the creation of interactive voice response systems by using web-based technologies. It enables dynamic responses, telephony integration, and real-time data access. For example, Sobot’s self-service IVR uses VXML to provide multilingual support and smart call routing, improving customer experiences.
What role does a VXML interpreter play?
A VXML interpreter processes VXML documents and executes their instructions. It acts as the bridge between the application logic and the voice user interfaces. This ensures accurate responses during voice interaction, enhancing the overall voice application experience.
Can VXML work with existing telephony systems?
Yes, VXML supports telephony integration, allowing it to work seamlessly with existing systems. This compatibility ensures businesses can implement VXML without overhauling their infrastructure. For instance, Sobot’s solutions integrate VXML with global telephony networks for efficient operations.
How does VXML improve customer service?
VXML enables personalized and efficient voice interaction by automating tasks and reducing wait times. It supports dynamic dialogs and error handling, ensuring smooth communication. Businesses like Sobot use VXML to enhance customer satisfaction by delivering accurate and timely responses.
See Also
Key Features Of Interactive Voice Response System Software
Understanding The Functionality Of IVR Voice Recognition Software
Comparative Analysis Of Leading Interactive Voice Response Software