The History and Evolution of Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency
Dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) technology revolutionized telecommunication by enabling faster and more efficient signaling. It generates tones when users press keys on a telephone keypad, with each key producing two distinct frequencies. This innovation replaced the slower pulse dialing system, allowing users to interact with automated systems and signal commands seamlessly.

The advantages of using DTMF technology extend beyond speed. It powers interactive voice response (IVR) systems, enabling self-service options like balance inquiries or preference changes. Companies like Sobot leverage DTMF in their Voice/Call Center solutions to enhance customer service. For example, Sobot's intelligent IVR system uses dual-tone multi-frequency signaling to route calls efficiently, improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The history and evolution of DTMF began in 1963 with its public introduction, marking a shift from rotary-dial systems to tone-based signaling. Its global adoption set the stage for modern telecommunication advancements.
The Origins of Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF)
Transition from Rotary-Dial Systems
Limitations of rotary-dial telephony
Rotary-dial telephony faced several challenges that hindered its efficiency.
- The mechanical dialing process was slow, requiring users to wait for the dial to return to its original position after each number.
- Errors during dialing were common, forcing users to restart the process.
These limitations became increasingly problematic as telecommunication systems expanded and required faster, more reliable methods for signal transmission.
The need for faster and more efficient signaling methods
The growing demand for improved telephony led to the search for alternatives to rotary-dial systems. The introduction of dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) technology addressed these issues by enabling faster and more accurate signaling. This innovation allowed users to interact with telecommunication systems more efficiently, paving the way for modern advancements like automated customer service and interactive voice response (IVR) systems.
Development of DTMF Technology
Research at Bell Labs and the introduction of Touch-Tone phones in 1963
Bell Labs played a pivotal role in the development of DTMF technology. Known as Touch-Tone, this system was introduced in 1963 and utilized push-button telephones to generate dual-tone signals. These signals replaced the slower pulse-based rotary system, marking a significant milestone in telecommunication. The debut of push-button phones at the 1962 World's Fair showcased this innovation, signaling a shift towards more user-friendly and efficient dialing methods.
Early adoption and public reception of DTMF technology
DTMF technology quickly gained acceptance after its public launch on November 18, 1963. Both the telecommunications industry and the general public embraced it for its speed and reliability. Its ability to support automated systems and enhance telephony efficiency contributed to its widespread adoption, setting the stage for its integration into global telecommunication networks.
Standardization and Global Adoption
Establishment of DTMF as an ITU-T telecommunication standard
The success of DTMF technology led to its standardization by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU-T). This recognition solidified its role as a universal method for controlling automated equipment and signaling user intent. The standardization ensured compatibility across different telecommunication systems, further driving its adoption.
Expansion to international markets and its role in global telephony
DTMF technology revolutionized global telephony by enabling interactive services like voicemail, telephone banking, and automated customer support.
- It became essential for remote equipment control and military communication systems.
- Businesses leveraged DTMF for menu navigation and secure transactions, such as credit card payments.
This widespread adoption highlighted its versatility and importance in modern telecommunication, including applications in platforms like Sobot's Voice/Call Center, which uses DTMF for efficient call routing and customer service.
How DTMF Technology Works
The Basics of Dual-Tone Signaling
Explanation of dual-tone frequencies and their generation
Dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) technology operates by generating two simultaneous sound frequencies whenever a key is pressed on a telephone keypad. These frequencies come from two distinct groups: low and high. For example, the low-frequency group includes tones like 697 Hz and 770 Hz, while the high-frequency group includes tones like 1209 Hz and 1336 Hz. Each key press combines one frequency from each group, creating a unique tone pair. This dual-tone system ensures accurate recognition of inputs, making it a reliable method for telephony signaling.

The role of the keypad in producing DTMF tones
The telephone keypad plays a crucial role in producing DTMF tones. Each button corresponds to a specific pair of frequencies. For instance, pressing the "5" key generates a combination of 770 Hz (low) and 1336 Hz (high). These tones are transmitted over the phone line, allowing systems to interpret the input. This mechanism forms the backbone of interactive voice response (IVR) systems, such as those used in Sobot's Voice/Call Center, where customers can navigate menus or input information seamlessly.
Technical Components of DTMF
Frequency pairs and their corresponding digits
DTMF technology relies on eight distinct frequencies divided into two groups:
- Low-frequency group: 697 Hz, 770 Hz, 852 Hz, 941 Hz
- High-frequency group: 1209 Hz, 1336 Hz, 1477 Hz, 1633 Hz
Each key on the keypad generates a unique combination of one frequency from each group. For example:
- The "1" key produces 697 Hz and 1209 Hz.
- The "9" key produces 852 Hz and 1477 Hz.
This systematic pairing ensures that every key press results in a unique signal, enabling precise communication between devices.
Signal transmission and decoding in telecommunication systems
When a user presses a key, the generated tones travel through the telecommunication network to the receiving system. Specialized equipment decodes these tones by identifying the unique frequency pair. This process allows systems to interpret commands, such as dialing a number or navigating a menu. Platforms like Sobot's Voice/Call Center leverage this technology to enable features like smart call routing and automated workflows, enhancing customer service efficiency.
Common Standards and Protocols
ITU-T recommendations for DTMF
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU-T) established Recommendation Q.23 as the primary standard for DTMF technology. This standard ensures consistency in tone generation and decoding across telecommunication systems worldwide. By adhering to these guidelines, DTMF remains a reliable and universally accepted signaling method.
Compatibility with modern telephony systems, including Sobot's Voice/Call Center
DTMF technology integrates seamlessly with modern telephony systems, including VoIP and cloud-based platforms. Sobot's Voice/Call Center exemplifies this compatibility by incorporating DTMF into its intelligent IVR system. This integration allows businesses to automate customer interactions, route calls efficiently, and provide secure input options for sensitive data, such as payment information.
Applications of DTMF in Customer Service
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Systems
Automating customer interactions using DTMF inputs
Dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) technology plays a vital role in automating customer interactions through interactive voice response (IVR) systems. By pressing keys on their phone, users generate DTMF tones that navigate automated menus. This allows customers to perform tasks such as checking account balances, making payments, or updating preferences without needing live agents.
For example:
- Pressing "1" might connect a caller to sales, while "2" could route them to billing.
- Customers can complete automated payments or access account details quickly and efficiently.
This automation reduces wait times and enhances user satisfaction by streamlining interactions.
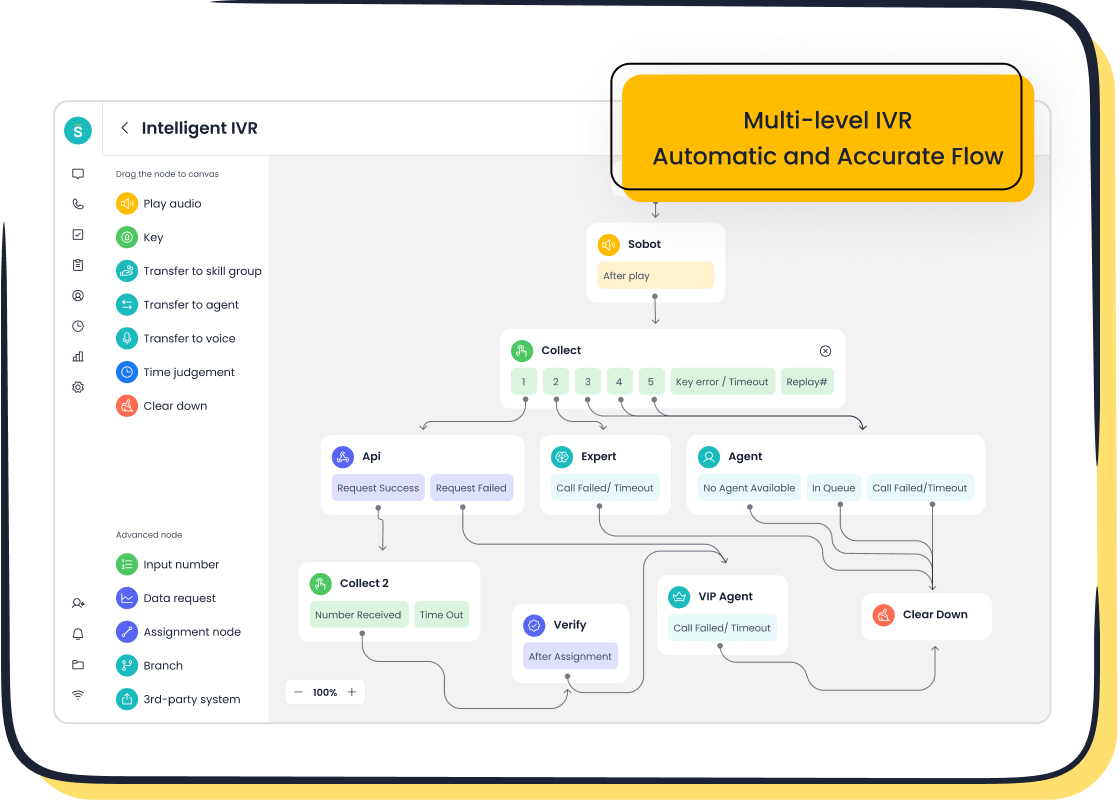
Examples of IVR use cases in Sobot's Voice/Call Center
Sobot's Voice/Call Center leverages DTMF technology to power its intelligent IVR system. Businesses can customize greetings, build menus, and route calls to the appropriate teams or agents. For instance, a retail company using Sobot's solution can enable customers to track orders or make payments directly through the IVR system. This not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances the overall customer experience.
Call Routing and Management
Efficiently directing calls to appropriate departments
DTMF tones are essential for call routing in contact centers. When callers interact with IVR menus, the tones generated by their key presses guide the system to direct calls to the correct department. This ensures that customers reach the right team, such as sales or technical support, without unnecessary transfers.
Enhancing customer experience through faster service with Sobot's smart call routing
Sobot's Voice/Call Center uses DTMF technology to enable smart call routing. The system automatically identifies the caller's needs based on their input and connects them to the most suitable agent or team. This reduces call handling time and enhances customer satisfaction. For example, Weee!, an online supermarket, improved its call routing efficiency by implementing Sobot's IVR system, achieving a 20% increase in agent productivity.
Secure Payment Processing
Using DTMF for entering sensitive payment information
DTMF payment technology allows customers to securely enter sensitive data, such as credit card numbers, using their phone's keypad. This method ensures that card details are transmitted digitally, preventing them from being overheard or recorded.
Ensuring compliance with PCI DSS standards in Sobot's solutions
Sobot's Voice/Call Center incorporates secure keypad pay-by-phone technology to protect customer data during transactions. By masking DTMF tones, the system ensures that sensitive information is not accessible to agents or stored in call recordings. This approach helps businesses comply with PCI DSS standards while providing a secure and seamless payment experience. For instance, customers can use Sobot's IVR payment technology to complete automated payments confidently, knowing their data is protected.
Challenges and Solutions in DTMF Technology
Security Risks and Vulnerabilities
Risks of eavesdropping and tone interception
Dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) technology, while efficient, presents certain vulnerabilities. The tones generated by key presses can be intercepted if recorded or stored improperly. This risk becomes critical during card-not-present transactions, where sensitive data like credit card numbers is transmitted. Wireless headsets and unsecured networks further increase the chances of eavesdropping. Additionally, call recordings may inadvertently capture sensitive information, exposing businesses to potential data breaches. These risks highlight the importance of implementing robust security measures to protect customer data.
Potential for fraud in sensitive transactions
Fraud remains a significant concern in DTMF-based payments. Cybercriminals can exploit intercepted tones to access sensitive information, leading to unauthorized transactions. For businesses handling high volumes of card payments, ensuring card payment security is essential. Without proper safeguards, these vulnerabilities can undermine customer trust and lead to regulatory penalties.
Compliance and Regulatory Issues
Importance of adhering to PCI DSS and other standards
Compliance with industry standards like PCI DSS is crucial for businesses using DTMF technology. These standards mandate strict measures to protect payment data, including masking tones and encrypting transmissions. Adherence ensures that sensitive information remains secure during transactions. Additionally, businesses must align with GDPR and other regional regulations to avoid legal repercussions and maintain customer confidence.
Challenges in maintaining compliance across systems
Maintaining compliance across diverse telecommunication systems poses challenges. Businesses must ensure that DTMF tones are masked during transmission to prevent eavesdropping. Digital transmission of card numbers must also avoid being captured in call recordings. These requirements demand advanced solutions that integrate seamlessly with existing systems while meeting regulatory standards.
Solutions and Best Practices
Implementing encryption and secure transmission methods
Encryption plays a vital role in safeguarding DTMF tones during transmission. By encrypting data, businesses can prevent unauthorized access and ensure secure payments. Masking tones during card payment entry further enhances data security, reducing the risk of interception. For example, Sobot's Voice/Call Center incorporates secure keypad pay-by-phone technology, ensuring compliance with PCI DSS standards while protecting customer information.
Leveraging Sobot's expertise for system optimization and compliance
Sobot offers advanced solutions to address DTMF-related challenges. Its Voice/Call Center platform integrates intelligent IVR systems that securely process payments and mask sensitive tones. By leveraging Sobot's expertise, businesses can optimize their systems for accuracy and compliance. Features like encrypted data transfer and seamless integration with existing systems help organizations navigate regulatory requirements while enhancing customer trust.
The Future of DTMF Technology
Integration with Modern Communication Systems
Compatibility with VoIP and digital telephony
Dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) technology continues to evolve alongside modern communication systems like VoIP and digital telephony. DTMF encoding transmits information through tones, each representing a digit or character. This method converts analog voice signals into digital signals, ensuring compatibility with digital networks.
VoIP systems, while primarily using Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) for signaling, include DTMF capacity to maintain interoperability with legacy systems. This integration allows businesses to leverage DTMF for tasks like menu navigation and secure payments. For example:
- DTMF enhances user interaction with IVR systems.
- It remains compatible with older telecommunication systems.
- It finds applications in industries like healthcare and finance.

Sobot's Voice/Call Center exemplifies this compatibility by seamlessly integrating DTMF into its intelligent IVR system, enabling businesses to automate customer interactions efficiently.
Enhancements in tone recognition and processing in platforms like Sobot's Voice/Call Center
Advancements in tone recognition are transforming DTMF technology. Machine learning algorithms now improve the understanding of human speech patterns, including tone, pitch, and rhythm. These innovations filter out background noise, optimizing DTMF performance in noisy environments.
Sobot's Voice/Call Center incorporates these advancements to enhance tone recognition accuracy. This ensures reliable call routing and secure data input, even in challenging conditions. By integrating speech recognition technology, Sobot also enables hands-free interactions, making its platform more accessible to users.
Emerging Use Cases
Potential applications in IoT and smart devices
DTMF technology is finding new applications in IoT and smart devices. For instance, the DTMFTalk application demonstrates how DTMF can control smart-home devices remotely. This innovation proves particularly useful in elderly care, where users can manage devices through phone calls.
The versatility of DTMF extends beyond telephony. It supports remote control systems and radio communication, showcasing its adaptability in modern technological applications. These emerging use cases highlight the potential of DTMF to enhance convenience and quality of life.
Expanding role in automated customer service solutions
DTMF remains a cornerstone of automated customer service. Its ability to navigate IVR menus and process secure payments makes it indispensable for businesses. Platforms like Sobot's Voice/Call Center leverage DTMF to streamline customer interactions. For example, Sobot's IVR system allows users to check account balances or make payments without agent assistance. This automation reduces wait times and improves customer satisfaction.
Addressing Future Challenges
Adapting to evolving security threats
As technology advances, DTMF faces new security challenges. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in tone transmission to intercept sensitive data. To counter this, DTMF technology integrates advanced solutions like AI and machine learning. These innovations enhance payment security by masking tones and encrypting transmissions.
Sobot's Voice/Call Center addresses these threats with secure keypad pay-by-phone technology. This feature ensures compliance with PCI DSS standards, protecting customer data during transactions.
Ensuring relevance in a rapidly changing tech landscape
DTMF must adapt to remain relevant in a fast-evolving tech environment. Its limitations, such as numeric-only input and lack of contextual understanding, restrict its use in complex interactions. Reliability issues over weak networks also pose challenges.
To overcome these obstacles, platforms like Sobot's Voice/Call Center combine DTMF with advanced technologies. By integrating AI-powered voicebots and speech recognition, Sobot enhances the functionality of DTMF systems, ensuring they meet modern demands.
Dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) technology has transformed telecommunication by replacing rotary dialing with faster, more reliable signaling. Its ability to generate unique tone pairs for each key press ensures secure and accurate communication. DTMF plays a vital role in interactive voice response (IVR) systems, enabling efficient call routing and self-service options. Businesses like Sobot leverage this technology in their Voice/Call Center solutions to enhance customer interactions and operational efficiency. For example, Sobot's intelligent IVR system uses DTMF to streamline call routing, reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction.
Looking ahead, advancements in DTMF technology, such as integration with speech recognition and machine learning, promise to enhance accessibility and accuracy. These innovations will expand its applications in areas like IoT, healthcare, and automated customer service. DTMF remains a cornerstone of modern communication, evolving to meet the demands of a rapidly changing technological landscape.
FAQ
What is DTMF technology, and why is it important?
DTMF technology generates unique tone pairs for each key press on a telephone keypad. It replaced rotary dialing, enabling faster and more accurate communication. This innovation powers IVR systems and secure payment processing. Businesses like Sobot use DTMF in their Voice/Call Center to enhance customer interactions and operational efficiency.
How does DTMF improve IVR systems?
DTMF technology allows users to navigate IVR menus by pressing keys on their phones. Each key press generates a unique tone pair, enabling precise menu navigation. Sobot's intelligent IVR system uses DTMF to route calls efficiently, reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction.
Is DTMF technology compatible with modern telephony systems?
Yes, DTMF integrates seamlessly with modern systems like VoIP and cloud-based platforms. For example, Sobot's Voice/Call Center incorporates DTMF into its IVR system, ensuring compatibility with digital networks while maintaining support for legacy systems.
How does DTMF ensure secure payment processing?
DTMF enables secure data entry by masking tones during transmission. This prevents sensitive information, like credit card numbers, from being intercepted. Sobot's Voice/Call Center complies with PCI DSS standards, offering secure keypad pay-by-phone technology for safe transactions.
What are some emerging applications of DTMF technology?
DTMF is expanding into IoT and smart devices. It enables remote control of systems like smart homes and healthcare devices. Platforms like Sobot's Voice/Call Center continue to innovate, integrating DTMF with AI-powered solutions for enhanced customer service and automation.
See Also
Comparative Analysis of Leading Customer Voice Software
Understanding Voice Analytics Technology in Call Centers
Key Features of Interactive Voice Response Software
