Why USB 2.0 Transfer Rates Are Still Relevant in 2025

USB 2.0 continues to play a vital role in 2025, offering a balance of compatibility, affordability, and practicality. Its 480 Mbps maximum Transfer Rate (TR) may seem modest compared to newer standards, but it remains sufficient for many tasks. Devices like keyboards, mice, and printers still rely on USB 2.0, making it indispensable for both home and office use. Its backward compatibility ensures seamless connections with modern USB ports, saving you from costly upgrades. For businesses, USB 2.0’s cost-effectiveness allows bulk purchases without breaking budgets. Even today, Sobot integrates USB 2.0 into its hardware solutions, ensuring reliable performance for essential tasks.
What Are USB 2.0 Transfer Rates?
Theoretical Maximum Speeds
Understanding the 480 Mbps claim.
The USB 2.0 protocol standard advertises a theoretical transfer speed of 480 Mbps, equivalent to 60 MB/s. This maximum transfer speed represents the upper limit of the data transfer rate under ideal conditions. However, achieving this rate in real-world scenarios is rare. The theoretical maximum transfer rate is calculated based on the USB protocol standard's design, which assumes no interference, perfect hardware, and optimal conditions. This figure highlights the potential of USB 2.0 but does not reflect typical performance.
How theoretical speeds differ from real-world performance.
The theoretical transfer speed of USB 2.0 often differs significantly from actual speeds due to various factors. Protocol overhead, such as error checking and data packet management, reduces the effective data transfer rate. Additionally, USB 2.0 operates in half-duplex mode, meaning data can only flow in one direction at a time. These limitations, combined with hardware constraints, result in average speeds closer to 30 MB/s. While this is far below the maximum transfer speed, it remains sufficient for many everyday tasks.
Real-World USB Transfer Speed
Typical USB 2.0 transfer rates in daily use.
In practical applications, USB 2.0 achieves transfer rates of around 37 MB/s on Windows systems. This speed allows you to transfer large files, such as high-resolution images, in seconds. For example, digital cameras benefit from USB 2.0's data transfer capabilities, enabling quick and efficient file sharing. External hard drives also rely on USB 2.0 to provide reliable storage solutions for users who need to manage large volumes of data.
Factors influencing real-world speeds.
Several factors impact USB transfer speed in real-world scenarios. The quality and length of the USB cable can affect the signal strength, reducing the data transfer rate. Hardware limitations, such as the performance of the connected storage device, also play a role. Older USB controllers may not fully utilize the USB 2.0 protocol standard, further limiting the maximum transfer speed. Despite these challenges, USB 2.0 remains a practical choice for many low-bandwidth applications.
Why Is There a Gap Between Theoretical and Actual Speed?
Protocol Overhead
How USB 2.0’s half-duplex nature affects speed.
USB 2.0 operates in half-duplex mode, meaning it can only send or receive data at one time, not both simultaneously. This design limits the actual transfer speed, as the protocol must pause to switch directions during communication. For example, when transferring files, the system alternates between sending data and receiving acknowledgments, which slows down the process. This limitation becomes more noticeable when handling larger files or multitasking with USB devices.
The impact of data packet management on performance.
The USB 2.0 protocol includes mechanisms like error checking and packet management to ensure data integrity. While these features improve reliability, they also introduce overhead that reduces actual speeds. Studies show that protocol overhead accounts for about 30% of the speed loss, with the maximum achievable bandwidth being around 53.248 MB/s instead of the theoretical 60 MB/s. This overhead arises from the time spent packaging data into smaller packets and verifying their accuracy during transmission.
Hardware and Device Limitations
Role of storage device performance in transfer rates.
The performance of the connected storage device plays a significant role in determining USB 2.0 speeds. For instance, a fast SSD connected via USB 2.0 may achieve read speeds of only 33 MB/s, far below its potential. This bottleneck occurs because the USB 2.0 interface cannot fully utilize the capabilities of modern storage devices. Similarly, older hard drives or flash drives often have slower read and write speeds, further limiting the actual transfer rate.
How older USB controllers contribute to slower speeds.
Legacy USB controllers, commonly found in older computers, can also cause performance issues. These controllers may not efficiently handle the USB 2.0 protocol, resulting in slower data transfer. For example, a modern external hard drive connected to an outdated USB controller might experience reduced speeds due to compatibility issues. This mismatch highlights the importance of hardware optimization in achieving better performance.
External Factors
Cable quality and length.
The quality and length of the USB cable significantly affect transfer speeds. Substandard cables with poor shielding can lead to signal attenuation, reducing the actual speed. Longer cables also experience more signal loss, which impacts performance. Using high-quality, shorter cables can help mitigate these issues and improve data transfer rates.
Signal interference and unstable connections.
External factors like electromagnetic interference (EMI) can degrade USB 2.0 performance. Devices such as microwaves or wireless routers emit signals that may interfere with USB connections, causing slow data transfer. Additionally, unstable connections due to loose ports or frayed cables can disrupt communication, further reducing speed. Ensuring proper shielding and stable connections can minimize these issues and enhance performance.
Scenarios Where USB 2.0 Remains Relevant

Compatibility with Legacy Devices
Why USB 2.0 is essential for older hardware.
USB 2.0 remains a lifeline for older hardware that lacks support for newer USB standards. Many legacy devices, such as older printers, scanners, and external storage drives, were designed with USB 2.0 as their primary interface. Upgrading these devices to newer standards is often impractical or impossible. By maintaining USB 2.0 compatibility, you can continue using these devices without needing costly replacements. Modern computers and laptops still include USB 2.0 ports, ensuring seamless connectivity for legacy systems.
Examples of devices still reliant on USB 2.0.
Many devices continue to rely on USB 2.0 for their functionality. These include:
- Keyboards and mice, which do not require high-speed data transfer.
- Basic office printers that prioritize reliability over speed.
- External storage devices designed for occasional use.
- Legacy systems that depend on USB 2.0 for compatibility.
This widespread reliance highlights the ongoing importance of USB 2.0 in today’s tech landscape.
Cost-Effectiveness
USB 2.0 as a budget-friendly option.
USB 2.0 offers a cost-effective solution for users who prioritize affordability over speed. It remains significantly cheaper than newer USB standards, making it an attractive choice for budget-conscious buyers. For example, businesses can purchase USB 2.0 peripherals in bulk at lower prices, reducing overall expenses. This affordability makes USB 2.0 ideal for basic office setups or home use, where high-speed data transfer is unnecessary.
When affordability outweighs speed requirements.
In scenarios where speed is not a priority, USB 2.0 provides excellent value. Devices like keyboards, mice, and basic printers perform their tasks efficiently without requiring faster transfer rates. For these applications, the cost savings of USB 2.0 outweigh the benefits of upgrading to newer standards. This balance of affordability and functionality ensures USB 2.0 remains relevant for many users.
Adequacy for Low-Bandwidth Applications
Use cases like keyboards, mice, and printers.
USB 2.0 excels in low-bandwidth applications where high-speed data transfer is unnecessary. Devices such as keyboards, mice, and printers rely on USB 2.0 for their connectivity needs. These peripherals require minimal bandwidth, making USB 2.0 a reliable and efficient choice. For example, a standard keyboard only sends small amounts of data, which USB 2.0 handles effortlessly.
Why USB 2.0 is sufficient for basic tasks.
For basic tasks, USB 2.0 provides all the speed and reliability you need. Whether you’re connecting a mouse for everyday navigation or a printer for occasional document printing, USB 2.0 delivers consistent performance. Its widespread compatibility ensures you can use these devices with almost any computer, making it a practical choice for low-bandwidth applications.
Tip: If you’re looking for affordable and reliable USB 2.0-compatible devices, consider exploring Sobot’s range of hardware solutions. They offer products designed to meet your everyday needs without breaking the bank.
Comparing USB 2.0 to Newer USB Standards

USB 3.x and USB-C
Key differences in transfer rate (tr) and functionality.
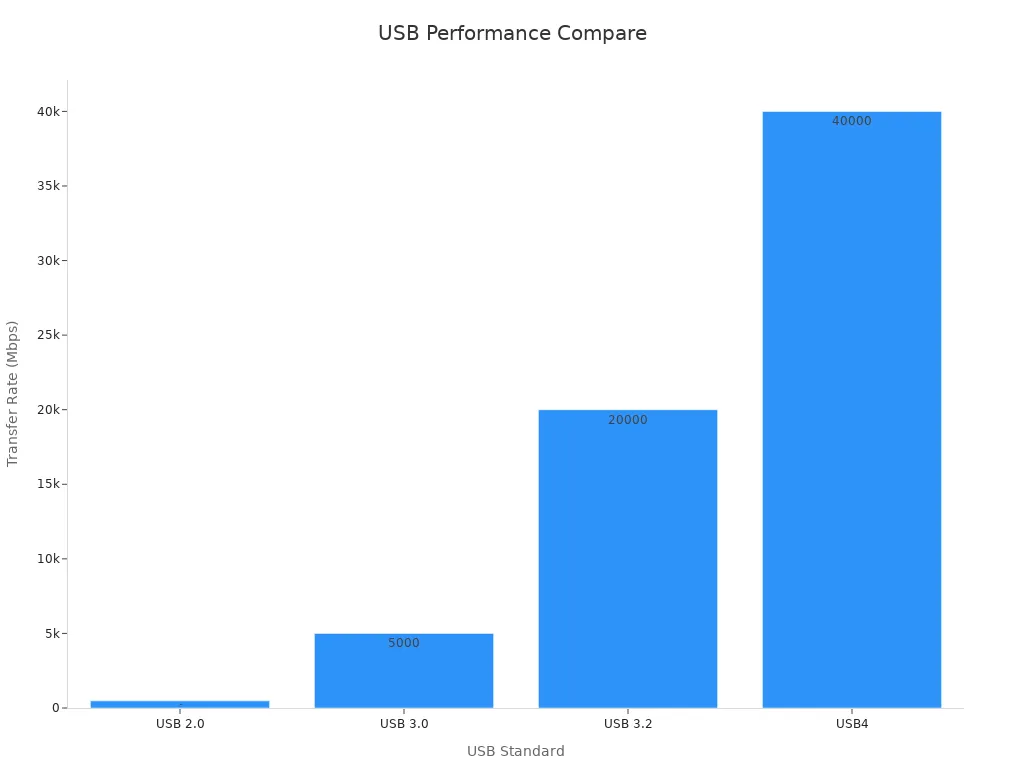
USB 2.0 and newer standards like USB 3.x and USB-C differ significantly in transfer rate (tr) and functionality. While USB 2.0 offers a maximum theoretical transfer rate of 480 Mbps, USB 3.0 delivers up to 5 Gbps, and USB4 reaches an impressive 40 Gbps. These advancements allow for faster file transfers, making USB 3.x and USB-C ideal for high-speed USB applications like external SSDs and video streaming.
The table below highlights key differences:
| USB Standard | Maximum Data Transfer Rate | Compatibility | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| USB 2.0 | 480 Mbps | USB 1.1 | Basic data transfer |
| USB 3.0 | 5 Gbps | USB 2.0 | Improved speed |
| USB 3.2 | 20 Gbps | USB 3.0, USB 2.0 | Multi-lane operation |
| USB4 | 40 Gbps | USB 3.2, USB 2.0, Thunderbolt 3 | Dynamic bandwidth allocation, USB Type-C connector |
USB 3.x and USB-C also introduce full-duplex communication, enabling simultaneous data sending and receiving. Enhanced power delivery supports faster device charging, making these standards more versatile. However, USB 2.0 remains sufficient for low-bandwidth tasks like connecting keyboards or mice.
When upgrading to newer standards is beneficial.
Upgrading to USB 3.x or USB-C is beneficial when you need faster transfer rates or advanced features. For instance, if you frequently back up large files or use external SSDs, the speed of USB 3.x can save you time. Similarly, USB-C’s reversible connector and compatibility with Thunderbolt 3 make it a future-proof choice for modern devices. However, for basic tasks, the USB 2.0 interface still provides reliable performance without the added cost.
Balancing Speed and Practicality
Why faster isn’t always better for every user.
Faster transfer rates may seem appealing, but they aren’t always necessary. For everyday tasks like connecting a mouse or printer, USB 2.0’s speed is more than adequate. Upgrading to a high-speed USB standard often comes with higher costs, which may not justify the benefits for low-bandwidth applications. You should consider your specific needs before investing in newer USB interfaces.
Trade-offs between cost, compatibility, and performance.
Choosing between USB standards involves balancing cost, compatibility, and performance. USB 2.0 remains the most affordable option, making it ideal for budget-conscious users. Its widespread compatibility ensures it works seamlessly with older devices and modern USB ports. On the other hand, USB 3.x and USB-C offer superior performance but at a higher price. For businesses or individuals who prioritize affordability over speed, USB 2.0 remains a practical choice.
Tip: If you’re looking for affordable USB 2.0-compatible devices, Sobot offers a range of reliable hardware solutions designed for everyday use.
The Future of USB 2.0 in a Modern World
Longevity and Support
How long USB 2.0 will remain in use.
USB 2.0 has proven its staying power over the years, and it will likely remain in use for the foreseeable future. Many devices, especially those designed for basic tasks, continue to rely on USB 2.0. Manufacturers still include USB 2.0 ports in modern computers and laptops, ensuring compatibility with older peripherals. This widespread adoption makes it difficult to phase out entirely. For example, industries like education and healthcare often use legacy systems that depend on USB 2.0 for their operations. These sectors prioritize reliability and cost-effectiveness, which USB 2.0 delivers consistently.
The role of manufacturers in maintaining support.
Manufacturers play a crucial role in keeping USB 2.0 relevant. By including USB 2.0 ports in their devices, they ensure compatibility with a wide range of peripherals. This approach benefits users who want to avoid upgrading their hardware unnecessarily. Companies like Sobot continue to design products that support USB 2.0, offering reliable and affordable solutions for everyday needs. Their commitment to backward compatibility helps extend the lifespan of USB 2.0, making it a practical choice for users worldwide.
Niche Applications
Industries and scenarios where USB 2.0 thrives.
USB 2.0 thrives in industries where simplicity and reliability are essential. In healthcare, home-based medical devices often use USB 2.0 for real-time health monitoring and data analysis. These devices rely on USB 2.0’s plug-and-play feature to ensure seamless connectivity. Similarly, the education sector benefits from USB 2.0’s affordability and compatibility, using it for devices like projectors and interactive whiteboards. These examples highlight how USB 2.0 meets the specific needs of niche applications.
Why simplicity and reliability still matter.
Simplicity and reliability make USB 2.0 indispensable for many users. Its straightforward design ensures easy setup and operation, even for non-technical users. For tasks like connecting a keyboard or transferring small files, USB 2.0 provides consistent performance without unnecessary complexity. This reliability is why industries continue to trust USB 2.0 for critical applications. Whether you’re using a medical device or a classroom projector, USB 2.0 delivers the functionality you need without compromising on ease of use.
USB 2.0 continues to hold its ground in 2025, proving its value through compatibility, affordability, and reliability. Despite advancements in USB technology, USB 2.0 remains a preferred choice for low-bandwidth applications like keyboards, mice, and printers. In 2023, it captured 60% of the USB devices market revenue, highlighting its dominance in data transfer and connectivity. Experts attribute this success to its robust performance and cost-effectiveness, which make it ideal for both personal and business use.
For businesses, USB 2.0 offers a budget-friendly solution, allowing bulk purchases of essential devices without compromising functionality. Its compatibility with older and newer devices ensures seamless integration, reducing the need for costly upgrades. Whether you’re connecting a legacy printer or a modern peripheral, USB 2.0 delivers the speed and reliability required for everyday tasks. Its simplicity and widespread adoption ensure it remains relevant in a rapidly evolving tech landscape.
FAQ
What is the main difference between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0?
USB 2.0 supports a maximum transfer rate of 480 Mbps, while USB 3.0 offers speeds up to 5 Gbps. This makes USB 3.0 ten times faster for transferring large files. However, USB 2.0 remains sufficient for low-bandwidth tasks like connecting keyboards or mice.
Can USB 2.0 devices work with USB 3.0 ports?
Yes, USB 2.0 devices are compatible with USB 3.0 ports. The connection works seamlessly, but the transfer speed will remain limited to USB 2.0’s maximum rate. This backward compatibility ensures you can use older devices with newer systems.
Why is USB 2.0 still widely used in 2025?
USB 2.0 remains popular due to its affordability and compatibility with legacy devices. Many peripherals, such as printers and medical equipment, rely on USB 2.0 for their functionality. Its simplicity and reliability make it a practical choice for basic tasks.
How can I improve USB 2.0 transfer speeds?
To optimize USB 2.0 performance, use high-quality cables and ensure they are not excessively long. Avoid signal interference by keeping USB devices away from sources like microwaves. Regularly update your device drivers to maintain compatibility and performance.
Are Sobot products compatible with USB 2.0?
Yes, Sobot designs its hardware solutions to support USB 2.0. This ensures compatibility with a wide range of devices, including legacy systems. Sobot’s products provide reliable performance for everyday tasks, making them a cost-effective choice for users.
See Also
Best VoIP Solutions To Consider In 2024
Leading Cloud Contact Center Tools Available In 2024
Comprehensive Reviews Of Contact Center Solutions For 2024
